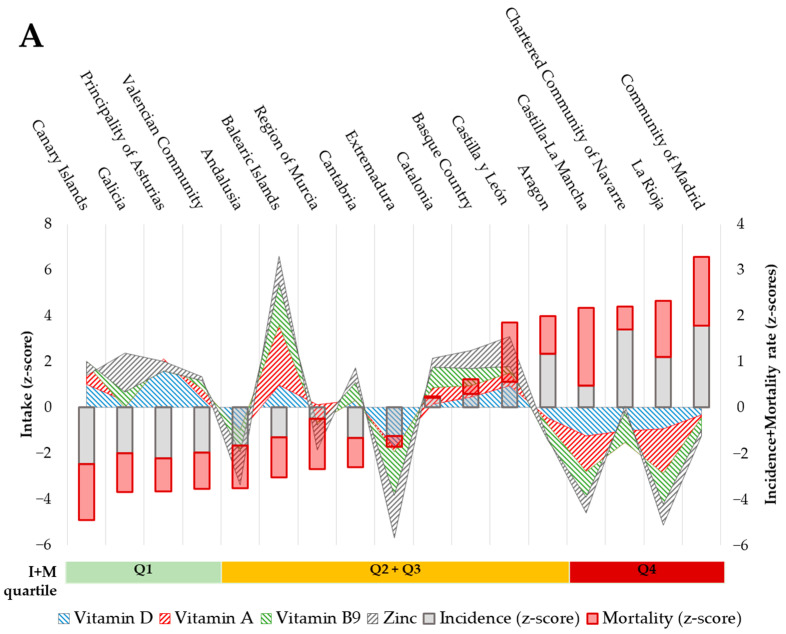
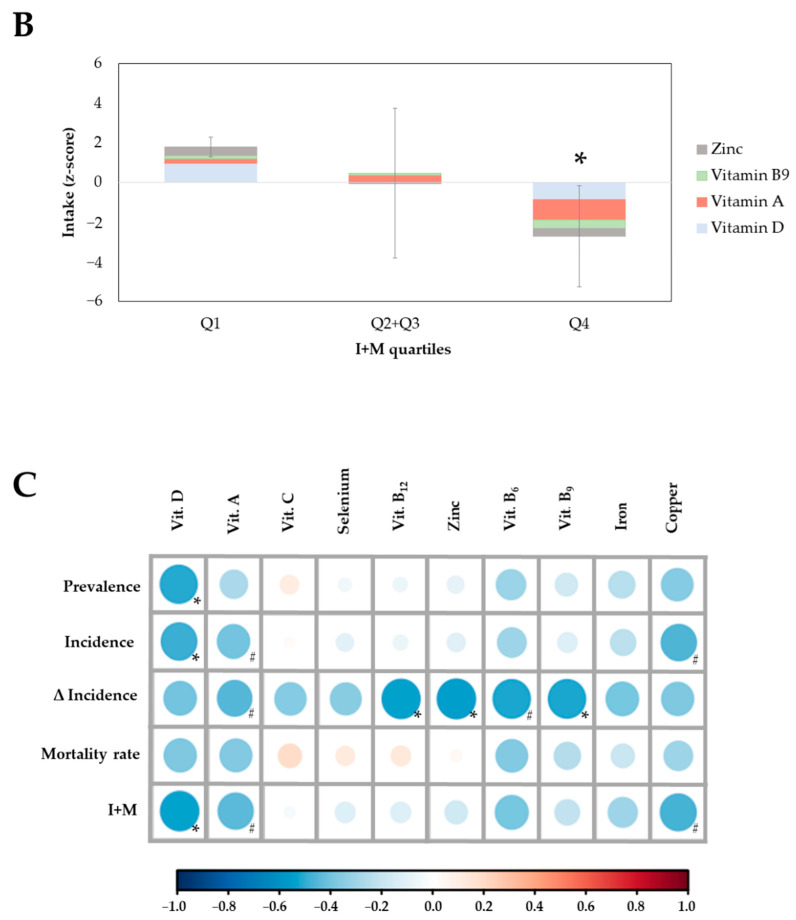
Figure 1.
Relationship between micronutrient intake (Z-score) and the impact of COVID-19 in the Autonomous Communities. (A) Cumulative intake of micronutrients—vitamin D (blue shading), vitamin A (red shading), vitamin B9 (green shading), and zinc (grey shading)—and the impact of COVID-19 (I + M index; Incidence (gray box); mortality (red box)) in Spanish ACs. ACs appear in increasing order of I + M index. ACs data are represented as the Z-score of the Spanish intake and classified by quartiles (Q) of the I + M index. (B) Mean ± standard deviation of the intake of vitamin D (blue box), vitamin A (red), vitamin B9 (green), and zinc (grey) in the ACs in quartile 1 (Q1), quartile 2 plus 3 (Q2 + Q3) and quartile 4 (Q4). Differences among means were assessed by Student’s T test comparing Q2 + Q3 vs. Q1 and Q4 vs. Q1, and p-value < 0.05 are indicated by * (C) Spearman correlation map of the intake level (Z-score) of each micronutrient and COVID-19 Prevalence, Incidence (COVID-19 cases per 100 k population), Incidence increase (∆ Incidence, in a 1.5-month period), Mortality rate (COVID-19 deaths per 1 M population) and, Incidence and Mortality index (I + M). # Spearman correlation p-value < 0.1; * Spearman correlation p-value < 0.05.