Figure 1:
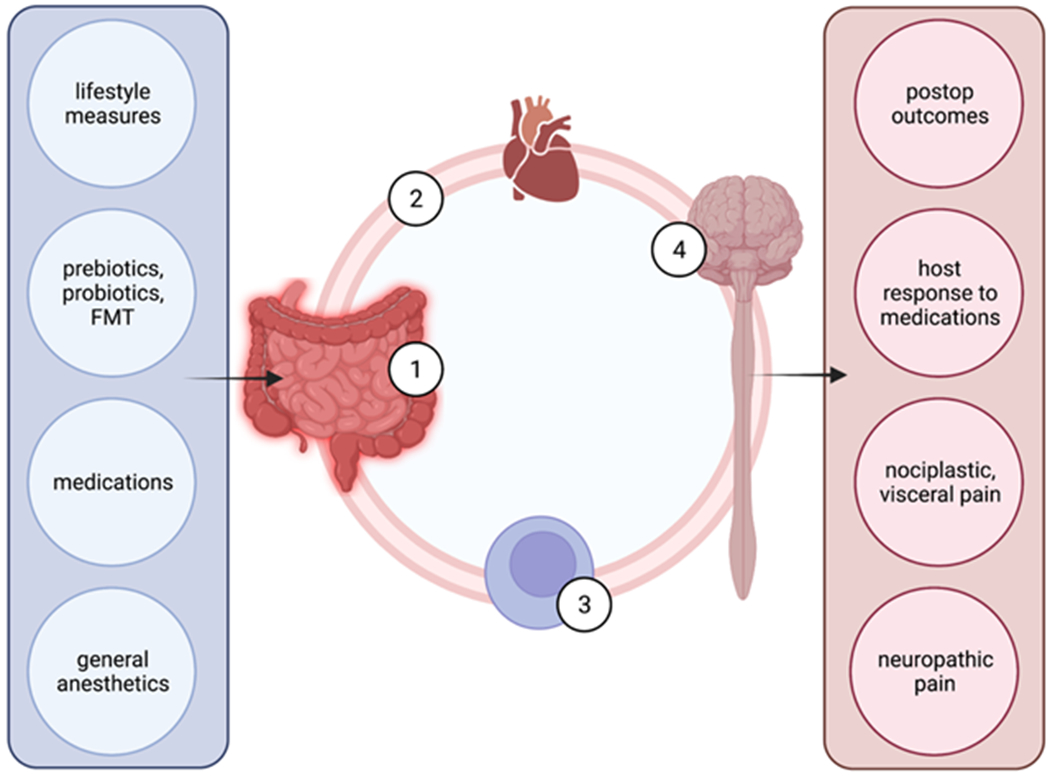
a schematic illustration of the putative mechanisms allowing the gut microbiome to affect nociception, pain modulation and postoperative outcomes. Left column lists major factors that influence gut microbiome (1). Through circulating metabolites (2) and cells, such as macrophages and T cells (3), gut microbiome influences the central nervous function (4). Right column lists functional phenotypes influenced by gut microbiome. (FMT – fecal microbiome transplantation; postop – postoperative]
