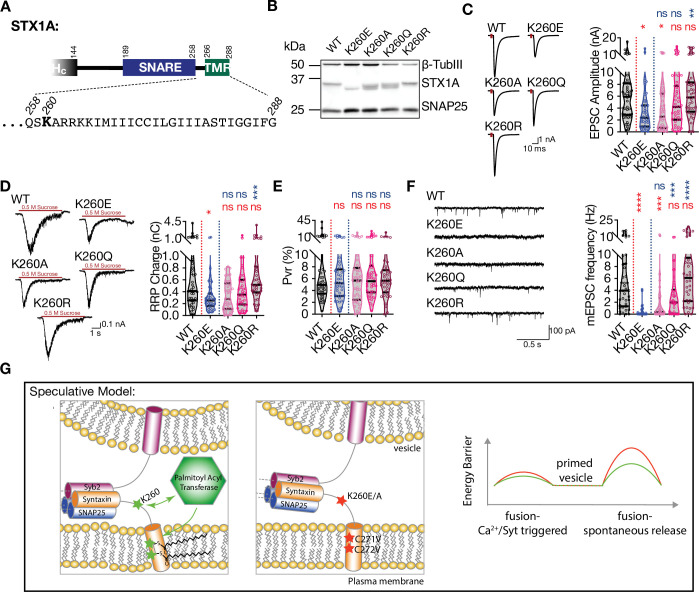
Figure 6. Palmitoylation of STX1A’s TMD depends on the presence of a basic residue at position AA 260 on its JMD.
(A) Position of the AA 260 on STX1A’s JMD. (B) Example image of SDS-PAGE of the electrophoretic analysis of lysates obtained from STX1-null neurons transduced with STX1AWT, STX1AK260E, STX1AK260A, STX1AK260Q, or STX1AK260R. (C) Example traces (left) and quantification of the amplitude (right) of excitatory postsynaptic currents (EPSCs) obtained from hippocampal autaptic STX1-null neurons rescued either with STX1AWT, STX1AK260E, STX1AK260A, STX1AK260Q, or STX1AK260R. (D) Example traces (left) and quantification of readily releasable pool (RRP) recorded from the same neurons as in (C). (E) Quantification of vesicular probability (Pvr) recorded from the same neurons as in (C). (F) Example traces (left) and quantification of the frequency (right) of miniature excitatory postsynaptic currents (mEPSCs) recorded from the same neurons as in (C). (G) Speculative model of the role of K260 and C271/C272 residues of STX1A. Left panel: the TMD of STX1AWT potentially adopts a tilted conformation that reduces the energy barrier for membrane merger. Palmitoylation of the TMD regulated by K260 contributes to its tilted conformation and thus to the facilitation of vesicle fusion. Middle panel: Inhibition of the palmitoylation of STX1A’s TMD either by K260E or CVCV mutations encumbers the TMD tilting and thus increases the energy barrier required for membrane merger. Left panel: the energy barrier is lower when STX1A-TMD is palmitoylated (STX1AWT,green) compared to that when STX1A-TMD is not palmitoylated (STX1AK260E or STX1ACVCV, red). Data information: the artifacts are blanked in example traces in (C and D). The example traces in (F) were filtered at 1 kHz. In (C–F), data points represent single observations, the violin bars represent the distribution of the data with lines showing the median and the quartiles. Red and blue annotations (stars and ns) on the graphs show the significance comparisons to STX1AWT and STX1AK260E, respectively. Non-parametric Kruskal-Wallis test followed by Dunn’s post hoc test was applied to data in (C–F); *p≤0.05, **p≤0.01, ***p≤0.001, ****p≤0.0001. The numerical values are summarized in source data.