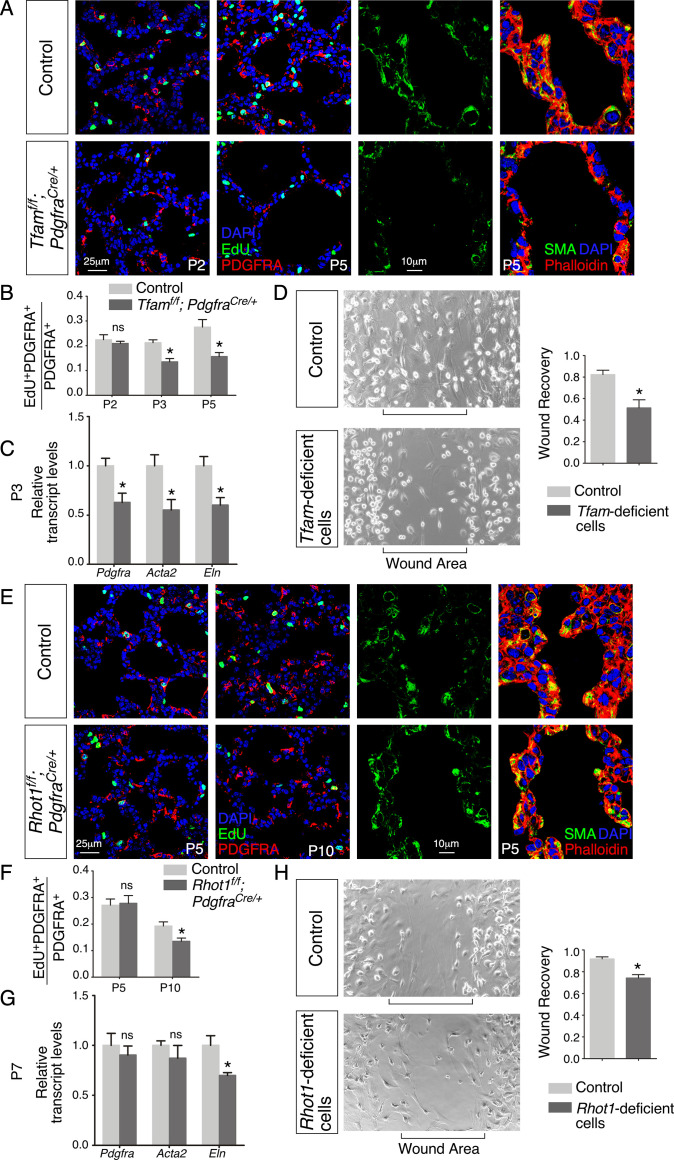
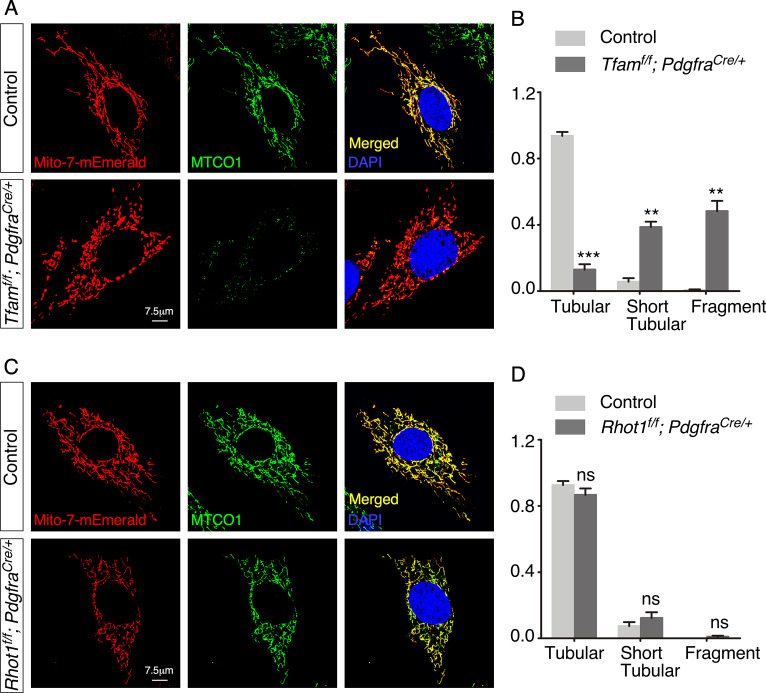
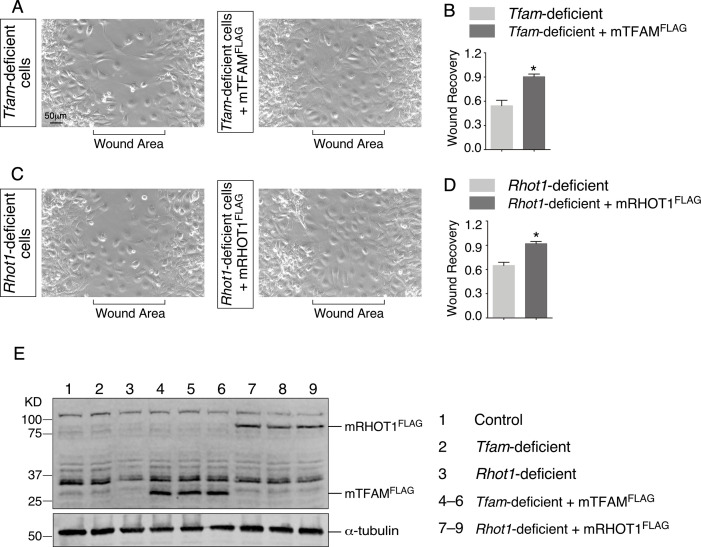
Figure 6. Loss of mesenchymal Tfam or Rhot1 compromises fibroblast/myofibroblast migration.
(A) Immunostaining of lungs collected from control and Tfamf/f; PdgfraCre/+ mice at postnatal (P) day 2 and 5, some of which were injected with EdU as indicated. (B) Quantification of fibroblast/myofibroblast proliferation in control and Tfamf/f; PdgfraCre/+ lungs at P2, P3, and P5 (n = 3 for each group). The rate of fibroblast/myofibroblast proliferation was calculated as the ratio of the number of EdU+ fibroblasts/myofibroblasts (EdU+ PDGFRA+) to the number of fibroblast/myofibroblasts (PDGFRA+). The percentage of proliferating fibroblasts/myofibroblasts was reduced in Tfamf/f; PdgfraCre/+ compared to controls at P3 and P5. (C) qPCR analysis of gene expression in control and Tfamf/f; PdgfraCre/+ lungs at P3 (n = 3 for each group). The expression levels of Pdgfra, Acta2, and Eln were significantly reduced in Tfamf/f; PdgfraCre/+ lungs compared to controls. (D) Wound recovery assays to assess the migratory ability of fibroblasts/myofibroblasts derived from control and Tfamf/f; PdgfraCre/+ lungs (n = 3 for each group). Within 36–48 hr, the wound area has been populated by migrating fibroblasts/myofibroblasts derived from control lungs. By contrast, fewer fibroblasts/myofibroblasts from Tfamf/f; PdgfraCre/+ lungs reached the wound area within the same time frame. Wound recovery by fibroblasts/myofibroblasts from control and Tfamf/f; PdgfraCre/+ lungs was quantified. (E) Immunostaining of lungs collected from control and Rhot1f/f; PdgfraCre/+ mice at P5 and P10, some of which were injected with EdU as indicated. (F) Quantification of fibroblasts/myofibroblasts proliferation in control and Rhot1f/f; PdgfraCre/+ lungs at P5 and P10 (n = 3 for each group). The percentage of proliferating fibroblasts/myofibroblasts was decreased in Rhot1f/f; PdgfraCre/+ compared to controls at P10. (G) qPCR analysis of gene expression in control and Rhot1f/f; PdgfraCre/+ lungs at P7 (n = 3 for each group). The expression levels of Eln were significantly reduced in Rhot1f/f; PdgfraCre/+ lungs in comparison with controls. (H) Wound recovery assays to assess the migratory ability of fibroblasts/myofibroblasts derived from control and Rhot1f/f; PdgfraCre/+ lungs (n = 3 for each group). Fewer fibroblasts/myofibroblasts from Rhot1f/f; PdgfraCre/+ lungs reached the wound area within the same time frame compared to controls. Wound recovery by fibroblasts/myofibroblasts from control and Rhot1f/f; PdgfraCre/+ lungs was quantified. All values are mean ± SEM. *p<0.05; ns, not significant (unpaired Student’s t-test).