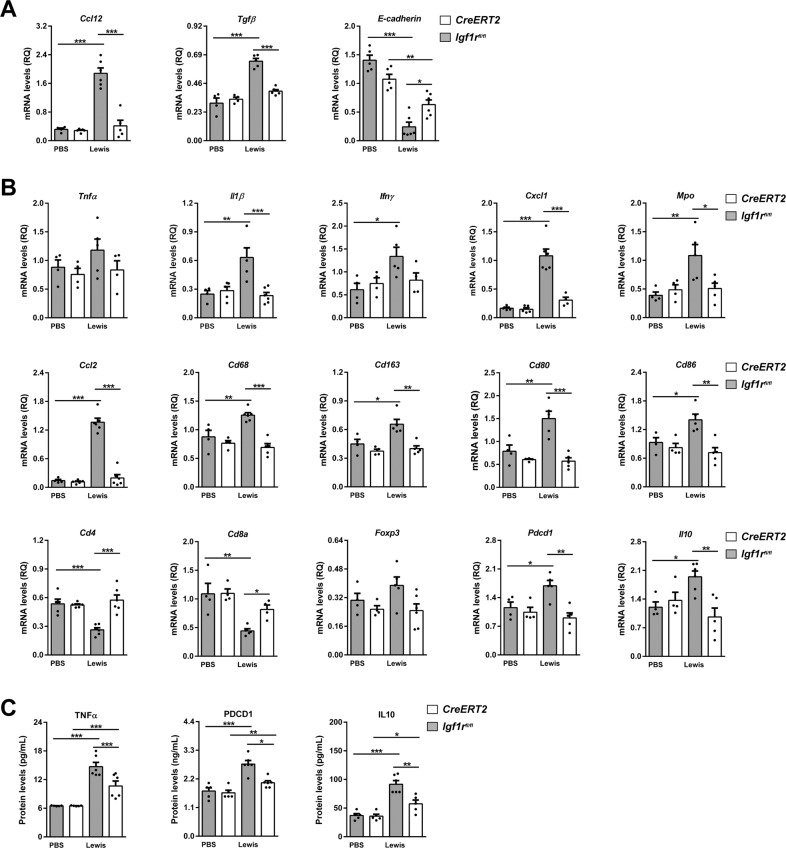
Fig. 6. IGF1R depletion diminishes expression of inflammation and lung tumor immunosuppression markers.
A Lung tissue mRNA expression of Ccl12 (recruitment of fibrocytes), Tgfβ and E-cadherin (epithelial-mesenchymal transition, EMT) normalized to 18 S expression (n = 4–6 mice per group) in lung homogenates from PBS- or LLC-challenged CreERT2 vs. Igf1rfl/fl mice. B Lung tissue mRNA expression levels of Tnfα and Il1β (Th1 inflammation), Ifnγ (T cell exhaustion), Cxcl1 (neutrophil chemotaxis), Mpo (neutrophils), Ccl2 (macrophage chemotaxis), Cd68 and Cd163 (tumor-associated macrophages, TAMs), Cd80 and Cd86 (dendritic cell activation), Cd4, Cd8a and Foxp3 (tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes, TILs), Pdcd1 (PD-1) (immunosuppression) and Il10 (immunosuppression), normalized to 18 S expression in PBS- or LLC-challenged CreERT2 vs. Igf1rfl/f mice (n = 4–6 mice per group). C TNFα, PDCD1 (PD-1) and IL10 protein levels in lung homogenates from PBS- or LLC-challenged CreERT2) vs. Igf1rfl/fl mice (n = 5–7 mice per group). Data are expressed as mean ± SEM. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001 (Dunn–Sidak test for multiple comparisons).