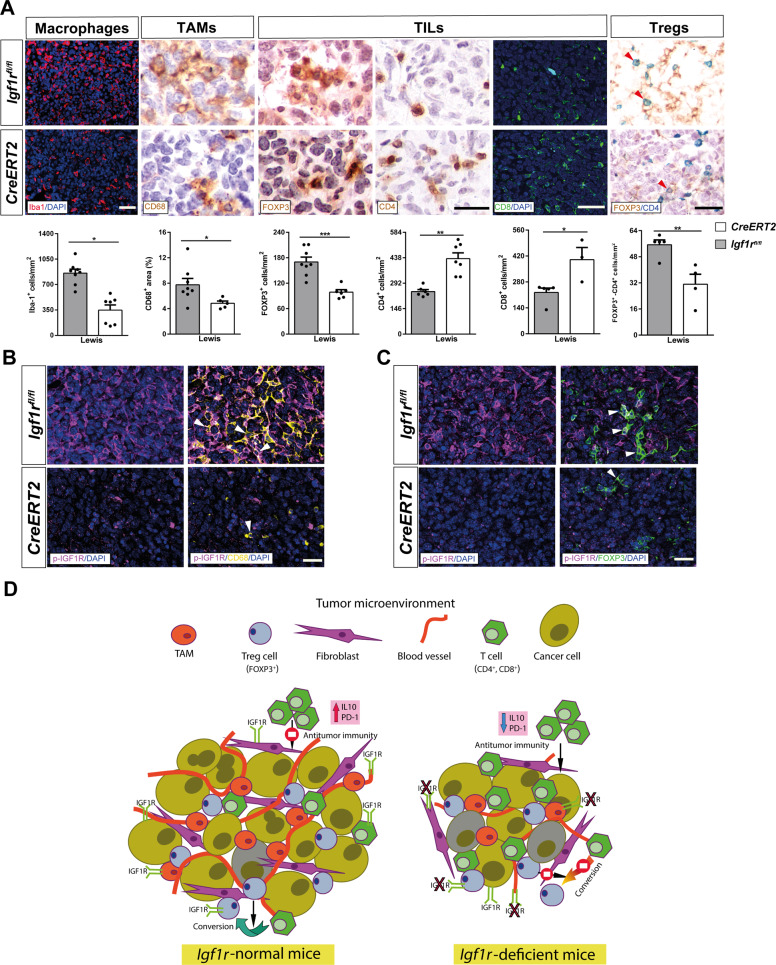
Fig. 7. IGF1R deficiency reduces inflammation and attenuates lung tumor immunosuppression.
A Representative immunostains and quantification of CD68+ (TAMs) (brown) area (%), Iba1+ (macrophages) (red), FOXP3+ (brown), CD4+ (brown), and CD8+ (green) (TILs), and FOXP3+CD4+ (Tregs) (green-magenta; red arrowheads indicate colocalization) cells per unit area (mm2) in the lung TME of LLC-challenged CreERT2 vs. Igf1rfl/fl mice (n = 3-6 mice per group; Scale bars: 30, 25, 40 and 25 µm, respectively). B, C Representative double immunostains for p-IGF1R and CD68 (magenta and yellow) and for p-IGF1R and FOXP3 (magenta and green; white arrowheads indicate colocalization) in the lung TME of LLC-challenged CreERT2 vs. Igf1rfl/fl mice (n = 4-5 mice per group; Scale bars: 30 µm). Quantifications were performed randomly in five different fields. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001 (Mann–Whitney U test or Student´s t-test for comparing two groups). D Proposed mechanism for reduced lung metastasis implantation and progression in IGF1R-deficient mice. Following induction of lung metastasis, IGF1R deficient mice exhibited reduced tumor burden, increased apoptosis, diminished proliferation, vascularization and EMT and fibrosis, as well as attenuated inflammation and immunosuppression. In accordance, IGF1R deficiency decreased expression of p-IGF1R in blood vessels, fibroblasts, TAMs and FOXP3+ TILs, key components in the lung TME. Specifically, IGF1R deficiency decreased the presence of TAMs and FOXP3+ TILs, which are known to promote lung tumor progression, as well as reduced IL10 and PD-1 levels, thus stimulating antitumor immunity. Moreover, decreased infiltration of FOXP3+ Tregs in IGF1R-deficient lungs could also reduce the conversion of antitumor CD4+ T cells into FOXP3+ Tregs.