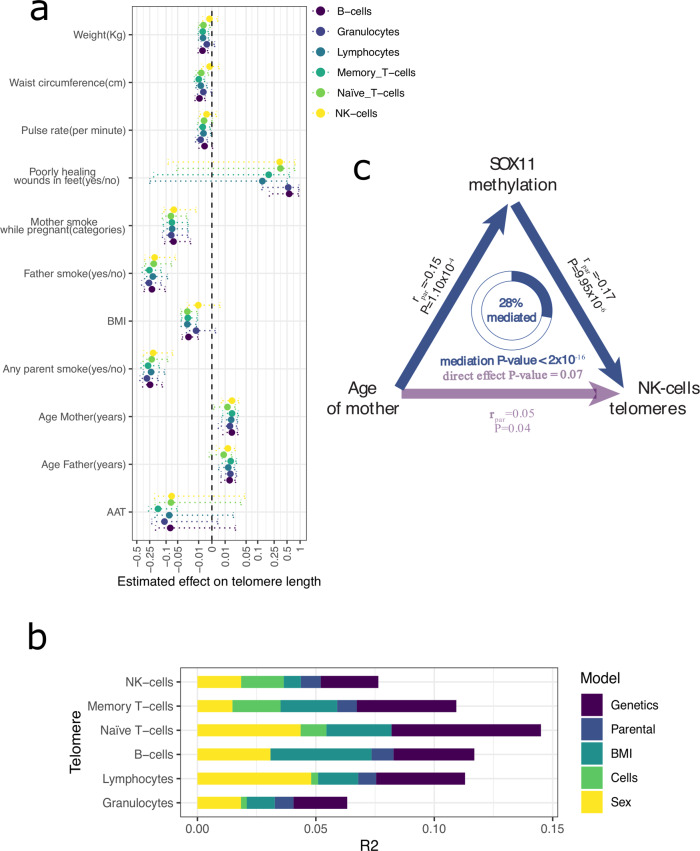
Fig. 3. Non-genetic factors contribute to telomere variation.
a Phenotype effect on telomere lengths of different cell types (with at least one significant association). Dashed lines show 95% confidence interval (estimate ± 2xSE). X-scale is symmetrical log-transformed (denominator constant = −2). BMI Body mass index, AAT Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Test. b Total variance of the telomere length explained after removing the effect of age. Only phenotypes associated with at least two cell types (FDR < 0.05) are used. Colour indicates the different partitions of variability. c Mediation effect of methylation of SOX11 in the maternal age effect on NK-cell telomere length variability.