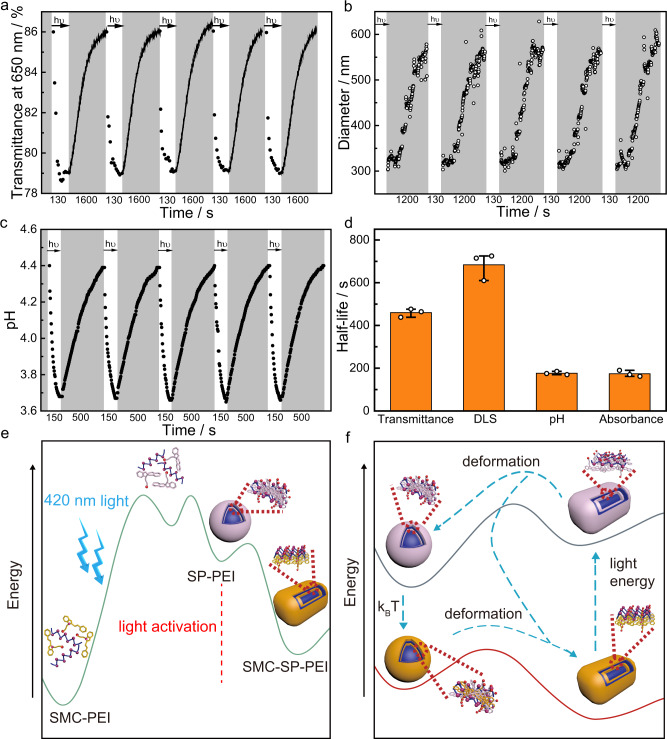
Fig. 4. Dissipative properties of the photodeformable supramolecular DSAs.
a Optical transmittance at 650 nm for 5 cycles between the SMC-PEI and SP-PEI dissipative process over time. The white areas represent the light-induced formation of SP-PEI nanoparticles and the gray areas represents the formation of SMC-SP-PEI nanoparticles, respectively. b Diameter variation during thermal deformation process from the SP-PEI to SMC-SP-PEI for 5 cycles over time measured by DLS. c pH variation for 5 cycles between the SMC-SP-PEI and SP-PEI dissipative process over time. The white parts represent the light-induced formation of SP-PEI and the gray parts represents the formation of SMC-SP-PEI nanoparticles, respectively. d Half-lives of the thermal deformation process from SP-PEI to SMC-SP-PEI exhibited by the transmittance at 650 nm, DLS, pH and absorbance at 424 nm. n = 3 independent experiments, with the bar data indicating mean ± SD ([SMC]initial = 0.225 mM, [PEI] = 5 μg mL−1). e Schematic representation of the energy variation of the light-activation process for the photodeformable DSAs. f Schematic representation of the energy variation in the photodeformable dissipative process of SP-PEI and SMC-SP-PEI.