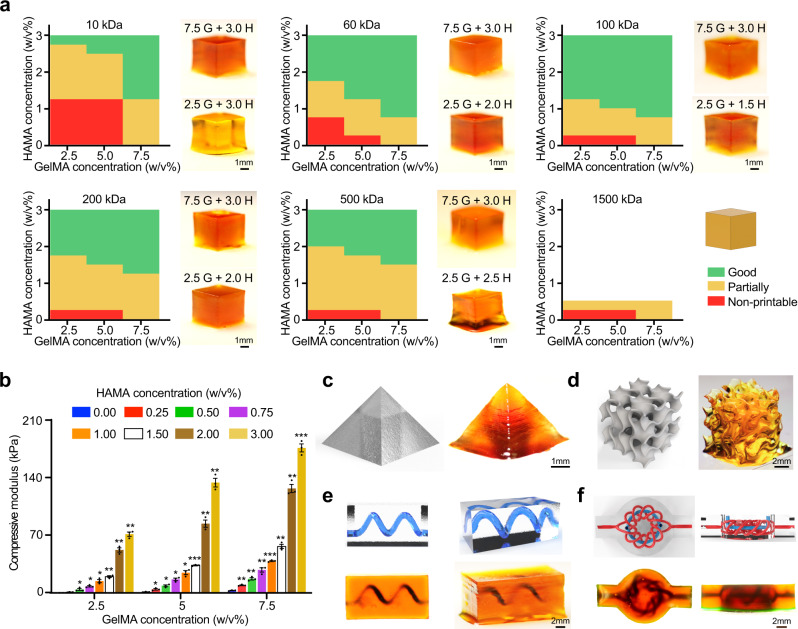
Fig. 2. Printability assessments of the GelMA/HAMA inks in DLP-based 3D printing.
a Printability maps and representative images of 3D-printed cubes using diverse enzyme-digestible inks, covering 2.5%, 5.0%, or 7.5% GelMA, and 0 to 3% HAMA (Mw = 10, 60, 100, 200, 500, or 1500 kDa). b Compressive moduli of samples fabricated from GelMA/HAMA inks across various formulations. n = 3; one-way ANOVA; *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 (compared with the respective control groups of 0% HAMA). Data are presented as mean values ± SDs. c–f Photographs showing 3D-printed constructs featuring sophisticated shapes and internal structures, using the GelMA/HAMA ink of 5.0%/3.0% (Mw of HAMA = 100 kDa) and corresponding digital models used for printing. c, Pyramid in the side view. d Gyroid in the side view. e Cuboid containing a spiral, perfusable channel in the top view and side view. f Torus knot (the digital design was obtained from11) in the top view and side view. a, and c–f, images are representatives of n = 3 independent experiments. G GelMA, H HAMA. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.