Fig. 4.
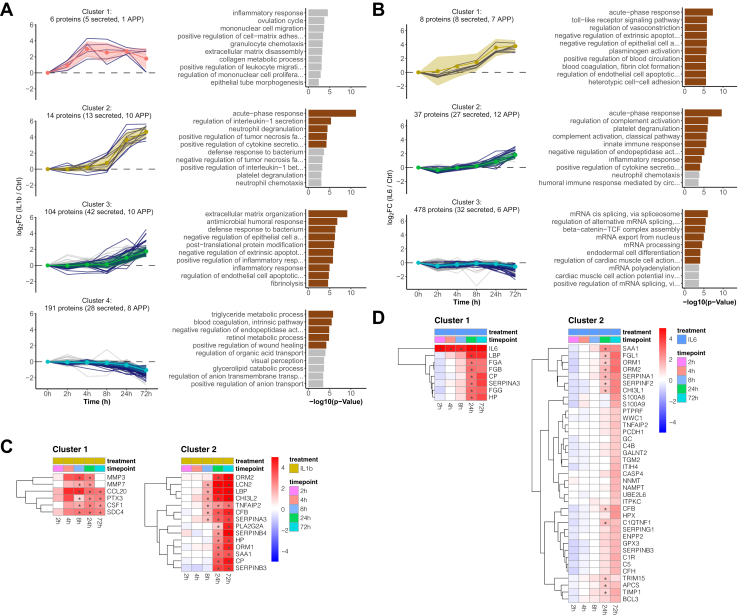
Time-dependent clustering of protein secretion discriminates early- and late-secretion events during the acute-phase response.A, time-resolved k-means cluster analysis of the interval-based secretomes of IL1b-treated HepaRG cells. Left panel, k-means clustering of all identified proteins (only clusters with time-dependent changes are shown here, for all clusters see supplemental Fig. S5). Clustering was performed by using proteins annotated to be secreted as training dataset. Colored ribbons indicate the mean log2 fold change ± SD in each cluster. Right panel, GO-term enrichment analysis showing the top ten biological processes for each cluster (brown bars indicate significant GO terms with p(Benjamini-Hochberg corrected) < 0.05). B, same as (A) for IL6 (only clusters with time-dependent changes are shown here, for all clusters see supplemental Fig. S6). C, heatmaps of time-dependent abundance change of all proteins grouped into cluster 1 and 2 from panel A of IL1b-treated HepaRG cells. Displayed are log2 fold changes to the respective time-matched control. Statistically significant changes are denoted with asterisks (∗). D, same as (C) for IL6-treated HepaRG cells. GO, gene ontology.