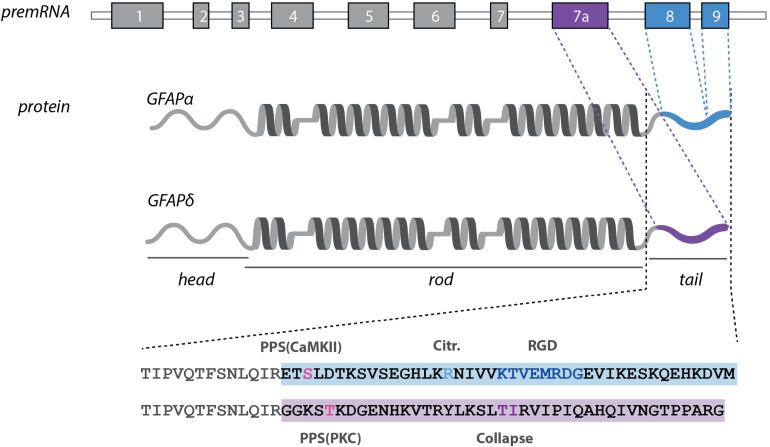
Figure 3.
The distinct features of the GFAPα and GFAPδ proteins. The GFAP protein consists of α-helical rod-domain (dark grey), flanked by a head- and tail-domain. The distinct tail-regions of the GFAPα and δ isoforms and the corresponding exons are marked in blue (GFAPα) and purple (GFAPδ). GFAPα contains an additional citrullination site (Jin et al., 2013) and a conserved RDG sequence (Chen and Liem, 1994). Both tail-regions have a different predicted phosphorylation site (Boyd et al., 2012). Collapse of GFAPδ has been assigned to T411 and T412 (Nielsen and Jørgensen, 2004). Abbreviations: aa = amino acids, PCS = predicted citrullination site, PPS = predicted phosphorylation site.