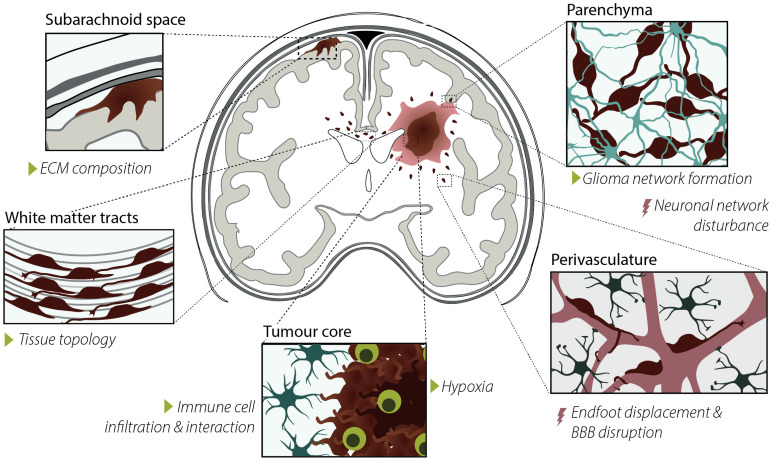
Figure 4.
Characteristics, drivers, and consequences of glioma cell invasion. Glioma cell invasion typically occurs along pre-existing structures in the brain, i.e. in the subarachnoid space and along the perivasculature and white-matter tracks. Glioma invasion is influenced by extracellular matrix (ECM) composition, tissue topology, immune cell interaction and infiltration, hypoxia, and glioma network formation, indicated with the green triangles. Consequences of invasion are neuronal network disturbances, astrocyte endfoot displacement, and blood-brain barrier disruption, indicated with the red lightning bolts.