Figure 1.
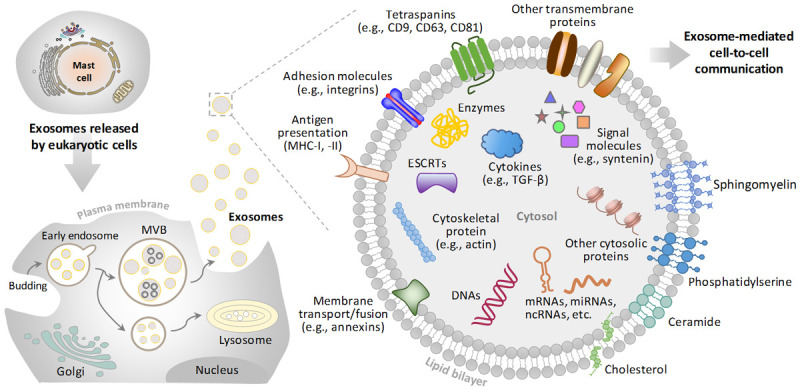
Schematic representation of biogenesis and overall composition of exosomes. Exosomes stem from later endosomes, generated by inward/inner budding from the plasma membrane (PM) or by fusion of internal multivesicular bodies (MVBs) with the PM in most of eukaryotic cells. Exosomes are vesicles with a phospholipid bilayer membrane and are enriched with a range of proteins, RNAs and DNA molecular cargoes. RNAs include mRNA, miRNA, ncRNA, and etc. Exosomes contain endosome-specific tetraspanins (CD9, CD63, CD81), adhesion molecules (e.g., integrins), antigen presentation (MHC-I, -II) and other transmembrane proteins on their membrane surfaces. Exosomes also contain types of cytosolic proteins, including ESCRTs, cytokines and signal molecules. Abbreviations: mRNA, messenger RNA; miRNA, microRNA; ncRNA, non-coding RNA; ESCRT, endosomal sorting complex required for transport; MHC, major histocompatibility complex.
