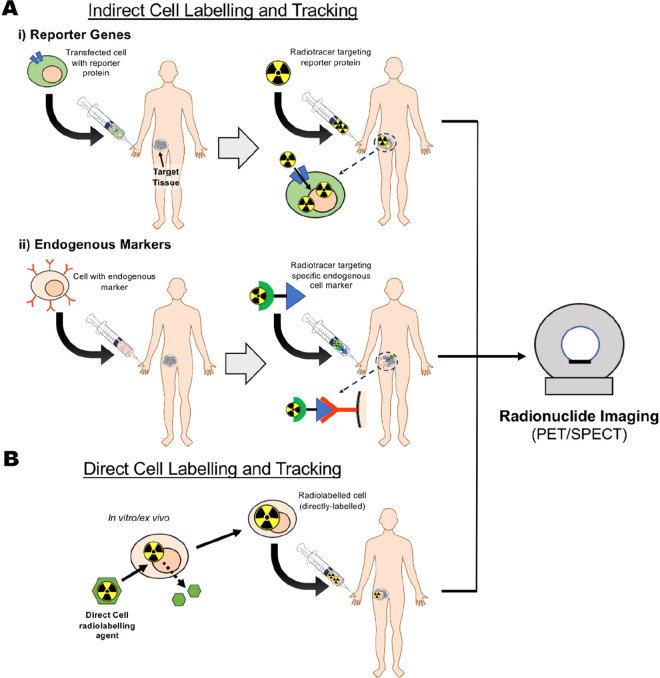
Figure 4.
Schematic representation of in vivo cell tracking methods using radionuclides. (A) (i) Indirect cell labeling and tracking; cells transfected with a reported gene are administered into the living subject, followed by a radiotracer targeting the specific reporter gene/protein. This radiotracer can be administered over the lifetime of a subject, allowing longitudinal imaging. (ii) Alternatively, cells expressing an endogenous marker (e.g., T-cell receptor) are administered into the living subject. Target uptake and distribution of the cells can then be imaged in vivo by administration of a radiotracer targeting the specific cell marker (e.g., radiolabeled antibodies). (B) Direct cell labeling and tracking. Cells are radiolabeled in vitro/ex vivo using a direct cell labeling agent. The cells are washed to remove unreacted radiotracer and then administered in the living subject for in vivo imaging using radionuclide imaging.