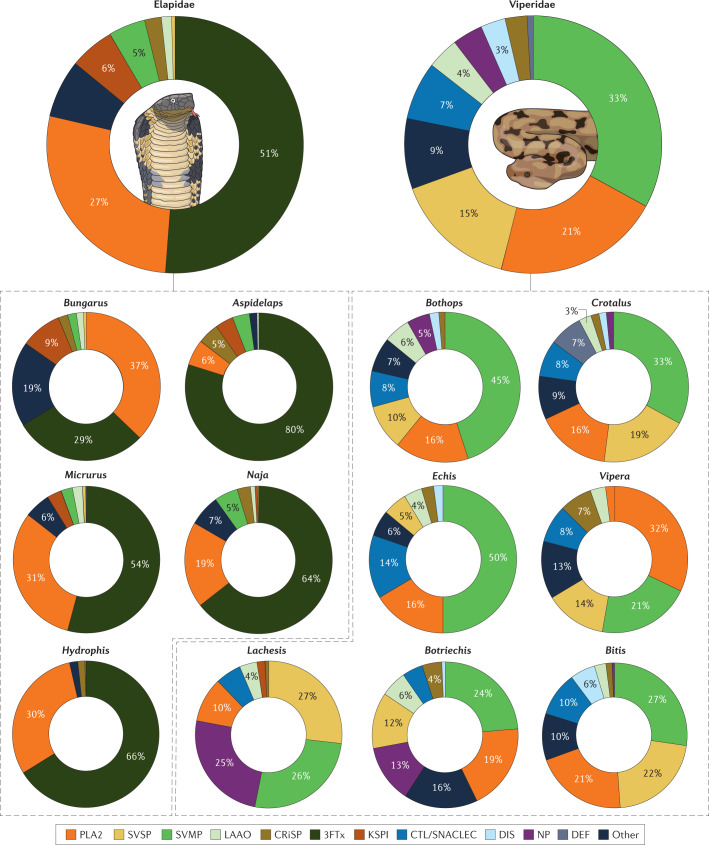
Fig. 1. Composition of the venom of snakes from the Elapidae and Viperidae families.
The large charts show the averaged composition of the venom of snake species from the Elapidae (elapids) or Viperidae (viperids) families. Each entry in the charts corresponds to a protein family, in which we group tens to hundreds of isoforms. Only protein families with an average abundance of >1% of the total venom proteome are represented, except for the SVSPs in elapids, which are included for comparison with the viperids, and defensins, which although seldom present, can be abundant in the venom of certain species. The distribution of the proportion of the most abundant protein families is shown in Supplementary Fig. 1. Data are from the proteomic studies of the past 15 years; 143 entries for 2007–2017 are from Isbister and Tasoulis’s database of snake venom proteomes7; we assembled the additional entries for 2017–2021 from the literature. The Atractaspididae and Colubridae snake families are not included in the study because most are non-venomous or their venoms are weak, not medically important and poorly studied (for venomics studies on colubrids see ref.15). Each species contributes with the same weight to the average; subspecies or species from different locations were averaged within the entry for the species. The entry ‘Other’ corresponds to unidentified components or components with an average abundance of <1%. The smaller charts decompose the snake venom composition at the genus level, which reveals the compositional diversity. Only the most well-studied genera are included, which comprise almost all the medically relevant snakes. Supplementary Table 1 details the composition of the venom of each species included in the study together with the relevant reference. 3FTx, three-finger toxin; CRiSP, cysteine-rich secretory protein; CTL/SNACLEC, C-type lectin and C-type lectin-like protein; DEF, defensin; DIS, disintegrin; KSPI, Kunitz-type serine protease inhibitor; LAAO, l-amino acid oxidase; NP, natriuretic peptide; PLA2, phospholipase A2; SVMP, snake venom metalloproteinase; SVSP, snake venom serine protease.