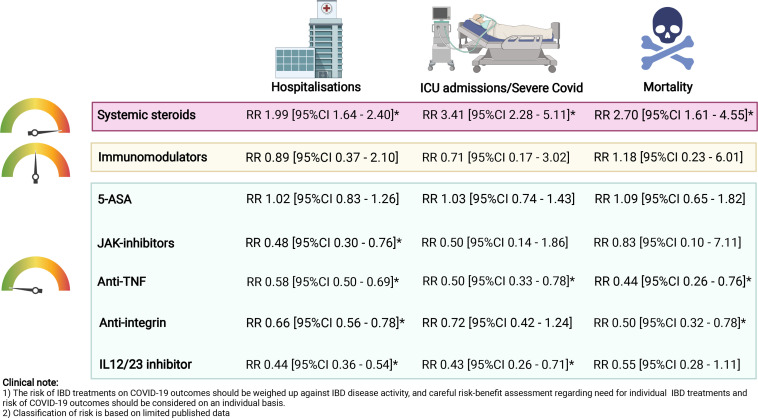
Figure 1.
Impact of IBD treatments on COVID-19 outcomes. Relative risks were calculated using multivariable logistic regression models comparing outcomes of COVID-19 from each medication class to those not treated with that medication. ICU admission encompassed composite outcomes made up by ICU admission, mechanical ventilation and mortality not due to COVID-19. The colours on the indicator represent the collective risk of IBD medications on COVID-19 outcomes: green=low risk, amber=moderate risk, red=high risk. *Indicates significant results where the 95% CI did not cross 1. Figure created with data from refs. 30 36 and using BioRender.com. 5-ASA, 5-aminosalicylic acid; IBD, inflammatory bowel disease; ICU, intensive care unit; JAK-inhibitor, Janus kinase inhibitor; RR, relative risk; TNF, tumour necrosis factor.