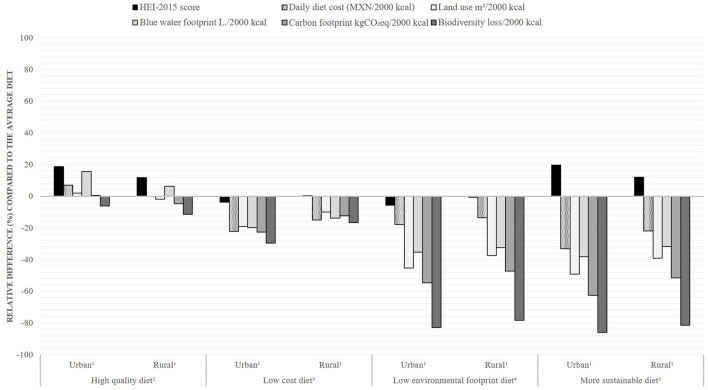
Figure 1.
Difference in dietary indicators of high-quality, low-cost, low-environmental footprint, and more sustainable diets relative to the average diet, by area of residence in Mexico. Values presented are the percentage difference in each dietary indicator (HEI-2015, cost and environmental footprint) relative to the average diet. 1Urban: more than 2,500 inhab; Rural: less than 2,500 inhab. 2Diets with HEI-2015 score above the overall median (54.2). 3Diets with daily diet cost below the median (50.9 MXN ≈ 2.6 USD). 4Diets with all environmental indicators below the median: land use (5.5 m2), blue water footprint (361 L), carbon footprint (3.4 kgCO2eq), and biodiversity loss (423 potential species loss × 10−10). 5Diets combining the criteria for high-quality, low-cost, and low-environmental-footprint diets. HEI-2015, Healthy Eating Index.