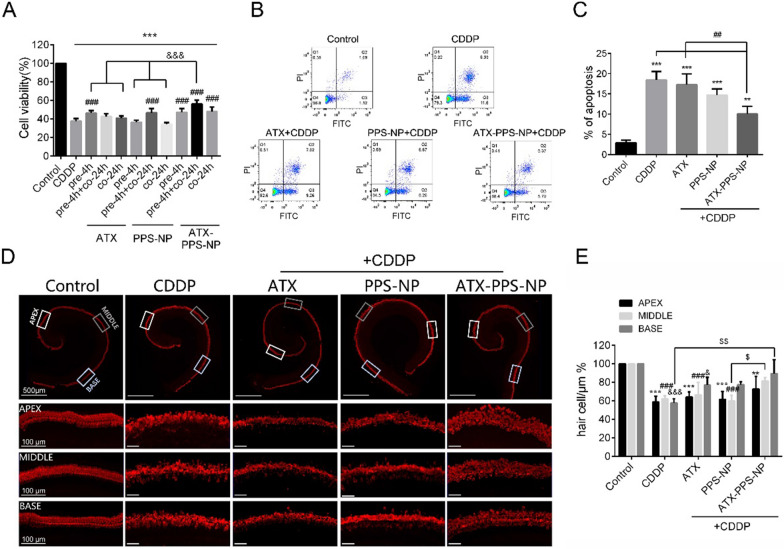
Fig. 4.
Cytoprotective and anti-apoptotic activity of ATX-PPS-NP against CDDP-induced toxicity in vitro. A A parallel comparison of cell viability in CDDP-treated HEI-OC1 cells with administrations of ATX (1 μg/ml), PPS-NP (drug free) and ATX-PPS-NP (1 μg/ml) in three types. *** p < 0.001 vs control, ### p < 0.001 vs CDDP, &&& p < 0.001 vs ATX-PPS-NP. B Flow cytometry showing the percentage of apoptotic cells labeled by Annexin V-FITC/PI double staining in ATX (1 μg/ml), PPS-NP (drug free) and ATX-PPS-NP (1 μg/ml) pretreated HEI-OC1 cells, followed by CDDP (60 μM, 24 h) exposure. C Quantifications of apoptotic cells. ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001 vs control, # p < 0.05, ## p < 0.01, ### p < 0.001 vs CDDP, &&& p < 0.001 vs ATX-PPS-NP. D Immunostaining of Myosin VIIa labeling hair cells in cochlea explants in control, CDDP (60 μM), ATX (1 μg/ml), PPS-NP (drug free) and ATX-PPS-NP (1 μg/ml) group. E Quantifications of hair cells in apex, middle and basal turn of cochlea explants. *, #, & p < 0.05 vs control, **, ##, && p < 0.01 vs control, ***, ##, &&& p < 0.001 vs control, $ p < 0.05 vs CDDP, $$ p < 0.01 vs CDDP