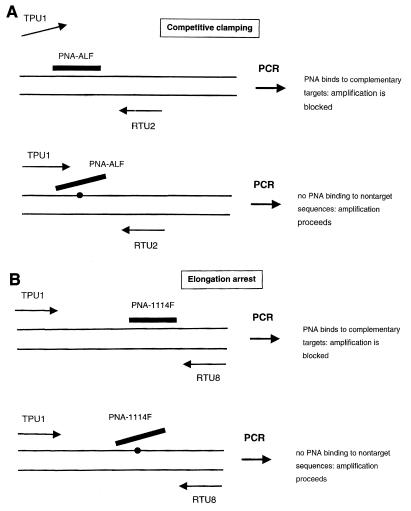
FIG. 3.
Schematic diagram of PNA-mediated PCR clamping of 16S rDNA amplification. (A) Competitive clamping: inhibition of PCR amplification by PNA-ALF-mediated exclusion of primer TPU1. (B) Elongation arrest: inhibition of PCR amplification by binding of PNA-1114F to an internal target sequence, which prevents readthrough by the Taq polymerase. In both cases amplification proceeds only if one or more base substitutions in the binding sites of appropriate PNA molecules are present.