Fig. 1 |. SpeB cleaves GSDMA.
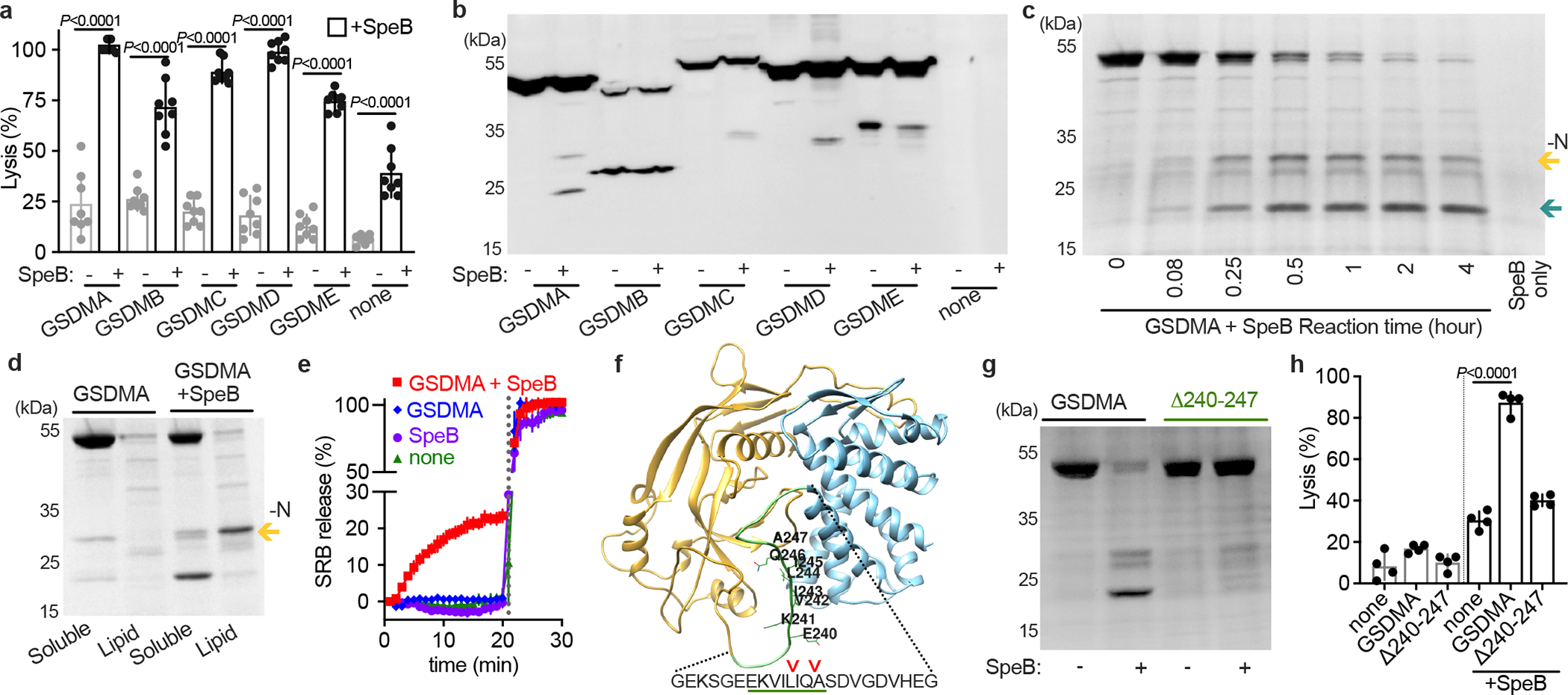
a, Cytotoxicity of each human GSDMs transfected ±SpeB in HEK293Ts. Data are the mean±s.d. of 8 technical replicates. b, Lysates of GSDM-transfected HEK293Ts incubated with SpeB and analysed by immunoblot. c, SDS–PAGE of recombinant human GSDMA cleavage by SpeB over time. GSDMA-N (gold arrow), GSDMA-C (teal arrow). d, PC:PE:cardiolipin liposome binding of GSDMA ±SpeB analysed by SDS–PAGE. GSDMA-N (gold arrow). e, Liposome leakage monitored by Sulforhodamine B (SRB) fluorescence on incubation with GSDMA ±SpeB. Detergent was added after 21 min (dotted line). f, hGSDMA model (Alphafold:Q96QA5) with SpeB cleavage sites identified by Edman sequencing indicated by arrows; GSDMAΔ240-247 deletion underlined in green. g, Cleavage of recombinant GSDMA or GSDMAΔ240-247 ±SpeB was analysed by SDS-PAGE. h, Cytotoxicity of HEK293Ts transfected with GSDMA or GSDMAΔ240-247 ±SpeB. Data are the mean±s.d. of 4 technical replicates. P values were calculated by two-tailed unpaired Student’s t-test (a,h) Data (a-h) are representative of three independent experiments. For gel source data, see Supplementary Figure 1.
