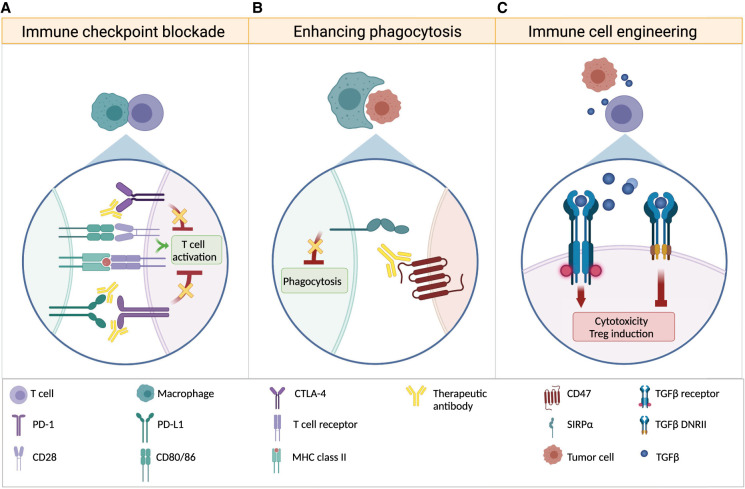
Figure 3.
Strategies to overcome immune suppression. (A) Monoclonal antibodies block immune checkpoint proteins that serve as intrinsic negative regulators of immune responses, allowing for continued immune cell activity. Antibodies directed against CTLA-4, PD-1, or its ligand PD-L1 inhibit the suppression of activated T cells. (B) CD47 is expressed on tumor cells and, upon binding to SIRPα on macrophages, prevents phagocytosis. Anti-CD47 antibodies block this interaction, allowing tumor cell phagocytosis by macrophages. (C) Genetic engineering can render immune cells resistant to tumor cell-induced suppression. Expression of a dominant-negative TGFβ receptor on immune cells prevents TGFβ-induced cytotoxicity as well as differentiation of Tregs and sequesters soluble TGFβ, preventing immunosuppressive TGFβ signaling in endogenous immune cells.