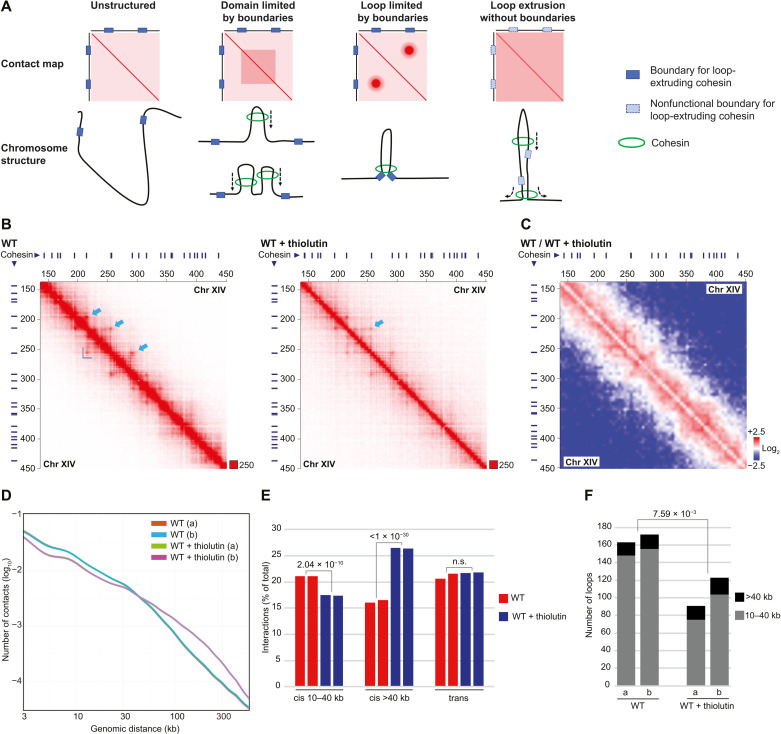
Fig. 1. Transcription inhibition removes cohesin loop extrusion barriers, triggering the formation of novel long-range cis interactions.
(A) Schematic illustration of cohesin loop extrusion and corresponding Hi-C contact maps in the presence of functional, or nonfunctional, loop extrusion boundaries. (B) Normalized Hi-C contact maps (2-kb binning) showing cis interactions along the arm of chromosome (Chr) XIV (150 to 450 kb from left telomere) in G2/M-arrested, untreated, and thiolutin-treated WT cells. Blue lines on top and to the left of the panels, cohesin binding sites; dark blue L shape within the panels, example of a domain; light blue arrows, examples of loop anchors. (C) Normalized Hi-C ratio maps (without binning) comparing chromosome cis interactions in untreated and thiolutin-treated G2/M-arrested WT cells along the same chromosomal regions as depicted in (B). (D) Contact probability plots as function of genomic distance comparing interactions in G2/M-arrested, untreated, and thiolutin-treated WT cells. (E) Quantification of cis and trans interactions in G2/M-arrested, untreated, and thiolutin-treated WT cells. (F) Number of loops anchored at cohesin sites in G2/M-arrested, untreated, and thiolutin-treated WT cells. (E) and (F) display results from two biological repeats, and statistical significance is indicated with P values from binominal tests. n.s., not significant.