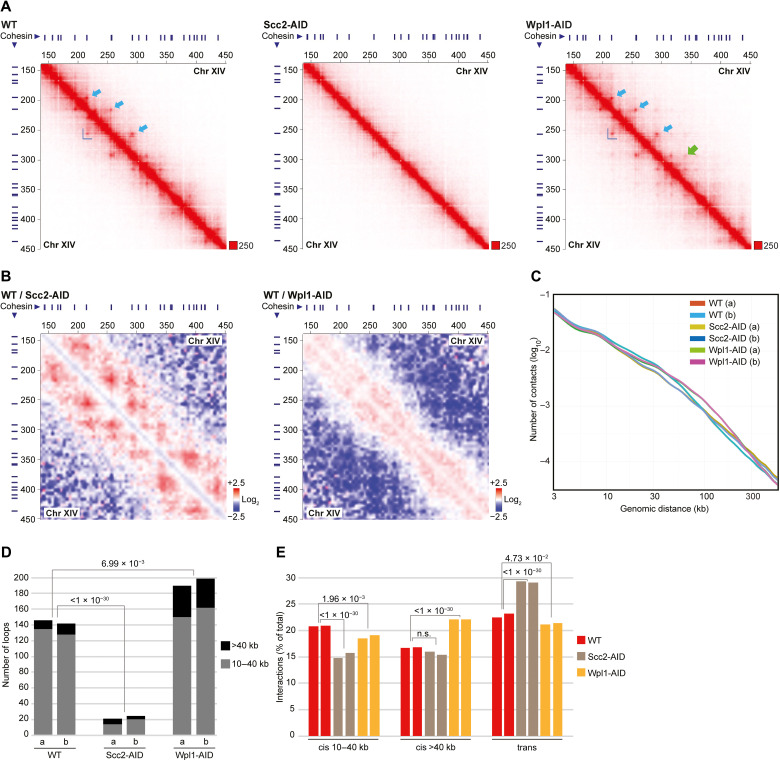
Fig. 2. Depletion of the cohesin loader Scc2 in G2/M phase disrupts chromosome loop formation.
(A) Normalized Hi-C contact maps (2-kb binning) showing cis interactions along the arm of chromosome XIV (150 to 450 kb from left telomere) in G2/M-arrested WT cells or in cells after depletion of Scc2 and Wpl1 (Scc2-AID, Wpl1-AID) in G2/M arrest. Highlights as in Fig. 1B), with an additional light green arrow showing a loop anchor only detected after Wpl1 depletion. (B) Normalized Hi-C ratio maps (without binning) comparing chromosome cis interactions in G2/M-arrested WT cells with those detected in cells depleted of Scc2 and Wpl1 (Scc2-AID, Wpl1-AID), along the same chromosomal regions as depicted in (A). (C) Contact probability plots as function of genomic distance displaying interactions in G2/M-arrested WT cells, or after depletion of Scc2 and Wpl1 (Scc2-AID, Wpl1-AID) in G2/M arrest. (D) Number of loops anchored at cohesin sites in G2/M-arrested WT cells, or after depletion of Scc2 and Wpl1 (Scc2-AID, Wpl1-AID) in G2/M arrest. (E) Quantification of cis and trans interactions in G2/M-arrested WT cells, or after depletion of Scc2 and Wpl1 (Scc2-AID, Wpl1-AID) in G2/M arrest. (D) and (E) display results from two biological repeats, and statistical significance is indicated with P values from binominal tests.