FIGURE 3.
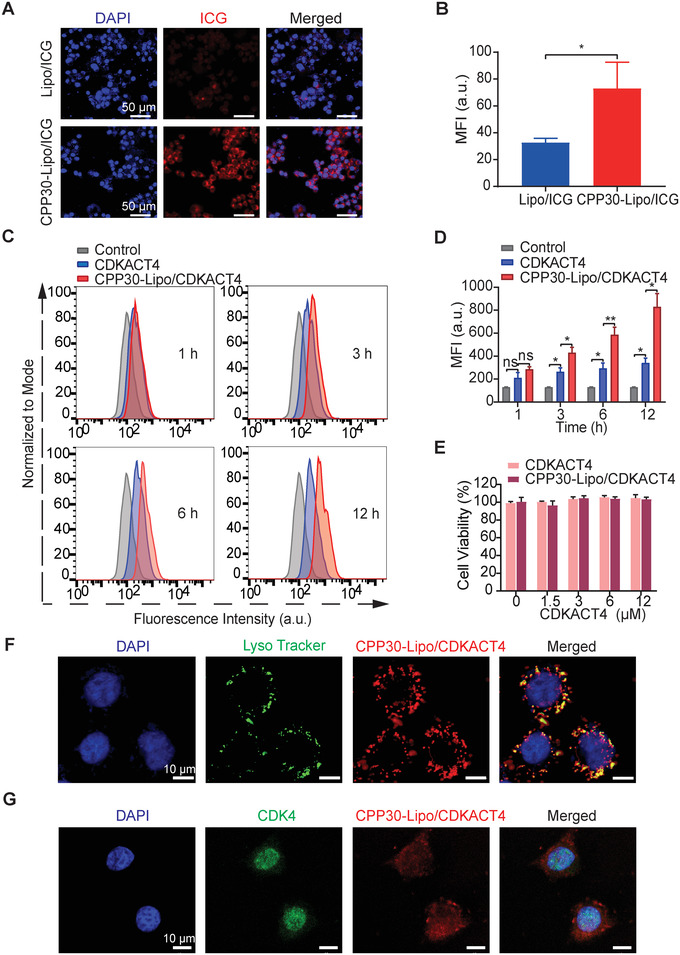
In‐vitro intracellular uptake and endosomal escape ability of CPP30‐Lipo/CDKACT4. (A, B) Representative fields under fluorescence microscopy (A) and mean fluorescence intensity (MFI, B) of MCF‐7 cells after incubation with Lipo/ICG or CPP30‐Lipo/ICG. Scale bar = 50 μm. C, Endocytosis of CDKACT4 and CPP30‐Lipo/CDKACT4 by MCF‐7 cells at 1, 3, 6, and 12 h post‐incubation as determined by flow cytometry. (D) Mean fluorescence intensity from flow cytometric analysis (C) at selected time points (n = 3, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01). (E) Viability of MCF‐7 cells after incubation with different concentrations of CDKACT4 and CPP30‐Lipo/CDKACT4 for 72 h (n = 5). (F) CPP30‐Lipo/CDKACT4 (red), and Lysotracker‐stained lysosomes (green) were imaged by confocal microscopy at 4 h after CPP30‐Lipo/CDKACT4 and MCF‐7 cell co‐incubation. Nuclei stained by Hoechst 33342 (blue). Scale bar = 10 μm. (G) Subcellular localization of CPP30‐Lipo/CDKACT4 (red) and endogenous CDK4 (green) in MCF‐7 cells as detected by indirect immunofluorescence and imaged by confocal microscopy. Nuclei stained by DAPI (blue). Scale bar = 10 μm
