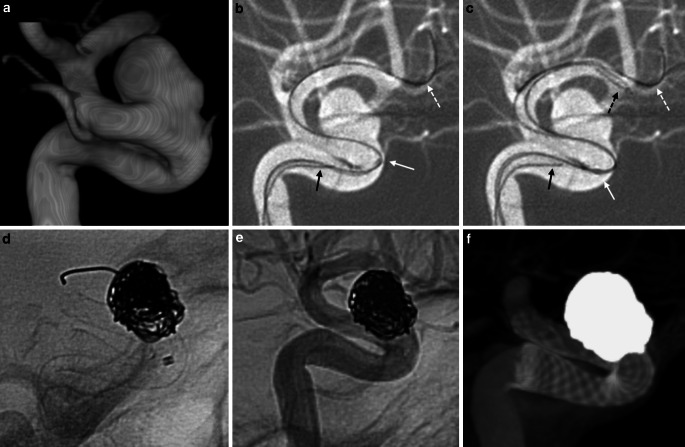
Fig. 2.
Female patient with a family history of aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage and incidental left paraophthalmic internal carotid artery. a 3D angiogram demonstrates the wide-necked aneurysm just distal to the origin of the ophthalmic artery. b Attempts to navigate a Marksman microcatheter over a Synchro 0.014in. microwire positioned in the left M2 were unsuccessful with the catheter tip being caught on the ophthalmic artery origin (white arrow). Note, a second microcatheter with a wire (black arrow) is being advanced into the aneurysm which was later used for coiling. c Adding an X‑pedion 0.010in microwire (black dashed arrow) within the Marksman microcatheter, which was advanced similarly into the left M2, provided the necessary support for the microcatheter to traverse across the ophthalmic segment for distal positioning. d–f A 4.75 × 18 mm Pipeline Flex embolization device was subsequently deployed and the aneurysm was coiled