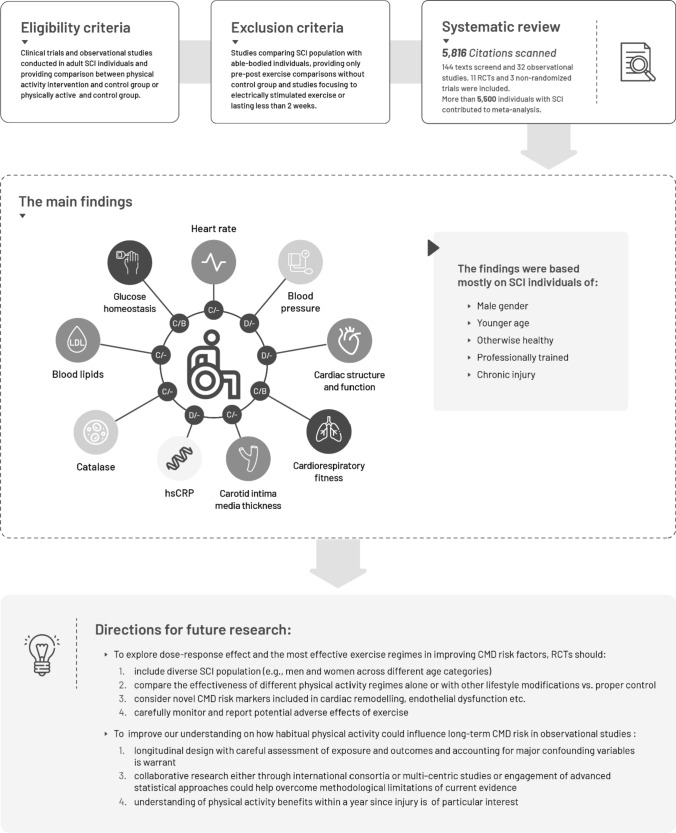
Fig. 3.
The illustrative summary of the most important findings of the current systematic review. White: No association observed in the meta-analysis. Dark grey: Results were supported by meta-analysis of cross-sectional studies and RCTs (i.e. glucose homeostasis). Grey: Results were supported by meta-analysis of cross-sectional studies only (i.e. blood lipids). Light grey: Results were significant only in cross-sectional studies but not overall (i.e. pooled estimates were significant only in analyses comparing para-athletes with sedentary individuals with SCI). Letters A-D refer to certainty of evidence as assessed using the GRADE approach: A: high certainty, B: moderate certainty; C: low certainty and D: very low certainty; First letter refers to certainty of evidence from cross-sectional studies, second letter refers to certainty of evidence from RCTs (missing letter for RCTs indicates that association was not supported by evidence form RCTs or that meta-analysis was not performed)