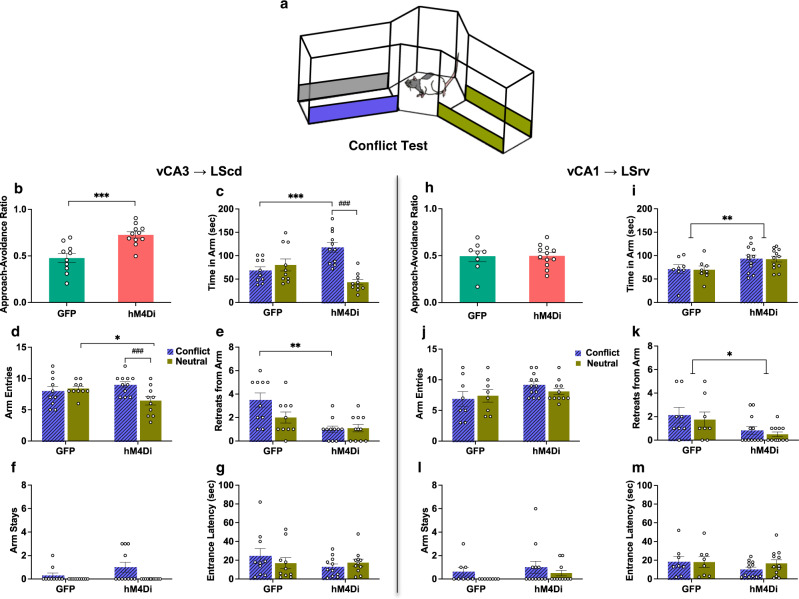
Fig. 3. vCA3 → LScd and vCA1 → LSrv circuit inhibition led to divergent responses during conflict test.
a Schematic of conflict test configuration with grey and blue bars depicting the combined appetitive and aversive cues in one arm, and green bars representing the neural cues in another arm. b, c vCA3 → LScd hM4Di animals showed potentiated approach (t16.18 = 4.17, p = 0.0005) driven by spending more time in the conflict vs. neutral arm, and more conflict arm time than GFP controls (Arm x Virus: F(1,19) = 16.42, p = 0.0004; post hoc arm t10 = 5.74, p = 0.0001; post hoc virus t19 = 3.66, p = 0.0009) d vCA3 → LScd hM4Di animals made more entries into the conflict than neutral, and less neutral arm entries than controls (Arm x Virus: F(1,19) = 8.89, p = 0.0160; post hoc arm t10 = 4.82, p = 0.0001; post hoc virus t19 = 2.44, p = 0.0392), and e retreated less from both arms than the controls (Virus: F(1,19) = 15.76, p = 0.0009; Arm x Virus: F(1,19) = 6.63, p = 0.0723; post hoc virus conflict t12.53 = 3.80, p = 0.0012; post hoc virus neutral t19 = 1.63, p = 0.0944) f Both vCA3 → LScd groups stayed in the conflict more than neutral (Arm: F(1,19) = 6.98, p = 0.0161), and g did not differ in latency to enter the arms (Lowest P: F(1,19) = 1.20, p = 0.2976). h vCA1 → LSrv hM4Di animals had equal approach-avoidance ratios (t11.96 = 0.06, p = 0.9548), i spent more time in both arms compared to controls (Virus: F(1,18) = 10.54, p = 0.0047), j had similar numbers of entries into the maze arms as the EGFP animals (Virus: F(1,18) = 2.46, p = 0.1340), k and fewer retreats (Virus: F(1,18) = 6.10, p = 0.0220). l Both vCA1 → LSrv groups trended toward more conflict arm stays (Arm: F(1,18) = 3.14, p = 0.0935), m and no difference in latency to enter either arm (Lowest P: F(1,18) = 1.86, p = 0.1893). Tests are unpaired two-sided t-tests (b, h) and two-way ANOVAs, followed by post hoc two-sided t-tests with Bonferroni-Holm correction for multiple comparisons (c–g, h–k). vCA3-hM4Di n = 11, vCA3-GFP n = 10, vCA1-hM4Di n = 12, vCA1-GFP n = 8. Data represent mean ± sem. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001. * denotes between-subject, and ♯ denotes within-subject comparisons. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.