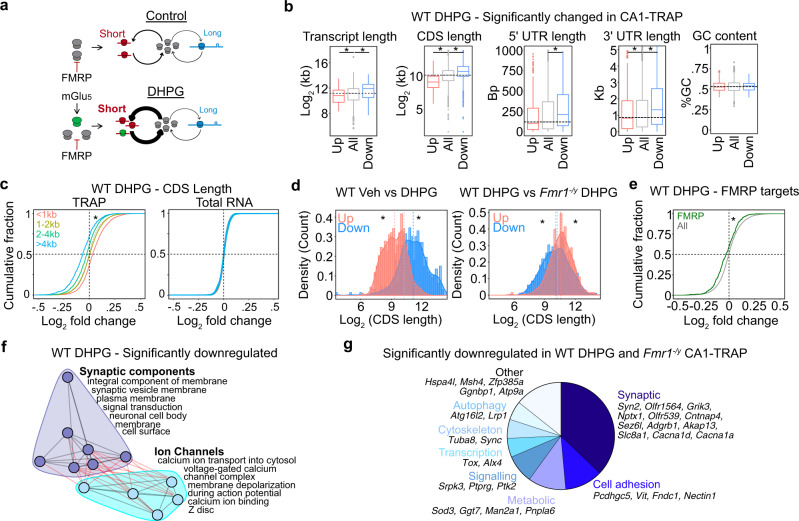
Fig. 5. Translation of long mRNAs is reduced in CA1 pyr neurons with induction of mGluR-LTD.
a Our model predicts that the increased ribosome production seen with mGluR-LTD will cause a similar length-dependent imbalance as seen in the Fmr1−/y translating population. b Analysis of the significantly changed population in WT DHPG CA1-TRAP shows a significant imbalance in transcript length, CDS length, 5’UTR length, and 3’UTR length that matches the basal Fmr1−/y CA1-TRAP population (transcript length: Kruskal–Wallis P = 2.105 × 10−14, Wilcoxon rank-sum test all vs up P = 6.042 × 10−5, all vs down P = 1.022 × 10−11, CDS length: Kruskal–Wallis *P < 2.2 × 10−16, Wilcoxon rank-sum test all vs up *P < 2.2 × 10−16, all vs down *P < 2.2 × 10−16, 5’UTR length: Kruskal–Wallis *P = 0.0005, Wilcoxon rank-sum test all vs up P = 0.0808, all vs down *P = 0.0006, 3’UTR length: Kruskal–Wallis *P = 0.000, Wilcoxon rank-sum test all vs up *P = 0.03821, all vs down *P = 0.0002, coding GC content: Kruskal–Wallis P = 0.9375). c A binned analysis shows that there is a CDS length shift in the TRAP fraction (two-sided KS test <1 kb vs >4 kb *P < 2.2 × 10−16) and no change in the total transcriptome (two-sided KS test <1 kb vs >4 kb P = 0.698). d Comparison of the top and bottom 500 differentially expressed transcripts in WT DHPG shows a significant effect of length (all vs up z = −17.831, *P < 2.2 × 10−16, all vs down z = 10.774, *P < 2.2 × 10−16). Comparison between WT DHPG vs Fmr1−/y DHPG reveals that the length shift is occluded in Fmr1−/y (all vs up z = 5.2982, *P = 1.16 × 10−7, all vs down z = −2.2827, *P = 0.02). e As predicted by their longer lengths, FMRP targets are reduced with DHPG in the WT CA1-TRAP population (two-sample z test, z = 5.333, P = 9.66 × 10−8). This change is not seen in the total transcriptome (two-sample z test, z = −2.039, P = 0.041). f Network analysis of the downregulated GO terms reveals a concentration of synaptic components and ion-channel clusters. g Analysis of the population significantly downregulated in both WT DHPG and Fmr1−/y CA1-TRAP fractions (P < 0.05) identifies 42 transcripts, many of which are involved in synaptic function.