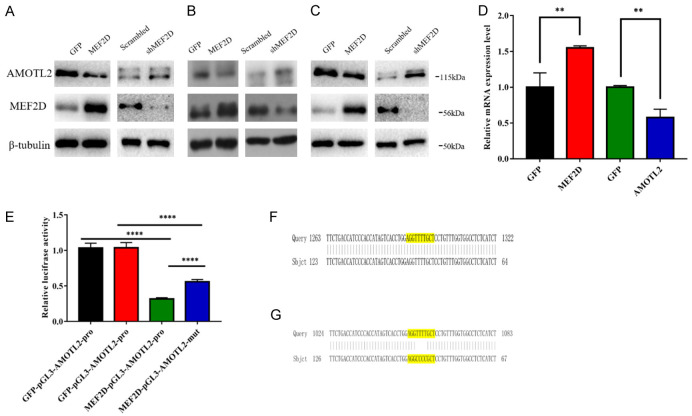
Figure 1.
MEF2D inhibited the expression of AMOTL2 and bound to the promoter of AMOTL2 in HCC cells. A. The expression levels of MEF2D and AMOTL2 were identified by western blot in HepG2 cells with overexpression or silencing of MEF2D and AMOTL2. B. The expression levels of MEF2D and AMOTL2 were identified by western blot in PLC/PRF/5 cells with overexpression or silencing of MEF2D and AMOTL2. C. The expression levels of MEF2D and AMOTL2 were identified by western blot in Huh7 cells with overexpression or silencing of MEF2D and AMOTL2. D. MEF2D and AMOTL2 mRNA were detected by qRT-PCR in PLC/PRF/5 cells overexpressing MEF2D. The data represent the means ± SDs of triplicate experiments. **, P < 0.01. E. pGL3 vectors controlled by wild type AMOTL2 promoter (pGL3-AMOTL2-pro) or MEF2-site-mutant ones (pGL3-AMOTL2-mut) was subjected to luciferase assay, under the overexpression of MEF2D or GFP. The data represent the mean ± SDs of three independent experiments. ****, P < 0.0001. F. Partial sequencing of pGL3-AMOTL2-pro vector showed that the yellow marker was MEF2 binding site. G. Partial sequencing of pGL3-AMOTL2-mut vector showed that the yellow marker was MEF2 binding site and mutant MEF2 binding sequence.