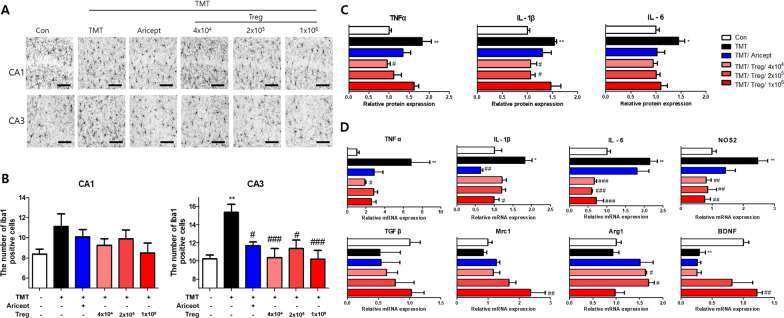
Fig. 5.
Treg inhibited pro-inflammatory factors via microglial activation in the brain of TMT-intoxicated. The expression of Iba1 was observed in the hippocampi of TMT-intoxicated mice using immunostaining (A). The number of Iba1-positive cells in CA1 and CA3 (B) was measured (n = 10–13 mice/group). The protein levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines, including TNFα, IL-1β, and IL-6, in the brain were measured using ELISA and calculated as a relative for Con (C) (n = 3–5 mice/group). The relative mRNA levels of pro-inflammatory microglia-associated markers, including TNFα, NOS2, IL-1β, and IL-6, and anti-inflammatory markers, TGFβ, Mrc1, Arg1, and BDNF in the brain were analyzed (D) (n = 3–5 mice/group). Data are presented as the mean ± SEM. Significance was determined by Tukey’s HSD (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 vs. the Con group and #p < 0.05, ##p < 0.01, ###p < 0.001 vs. the TMT group)