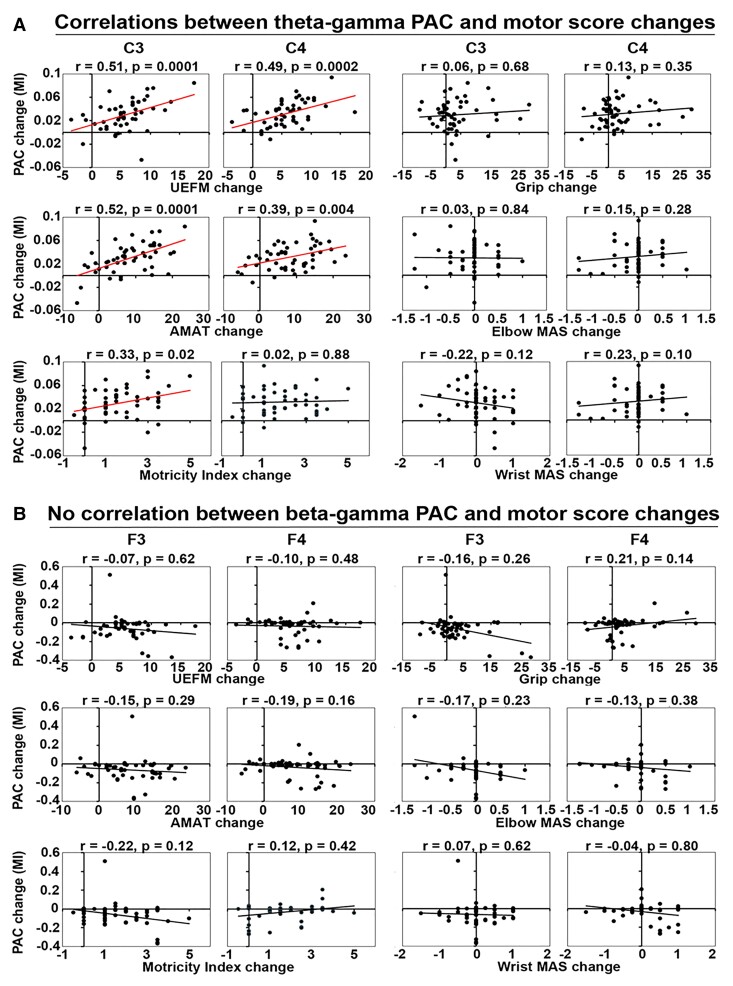
Figure 5.
Relationships between motor recovery and PAC change. Spearman rank correlations were run between changes in motor scores and theta–, beta–gamma PAC values across BCI therapy runs relative to Pre-BCI baseline (N = 51). Significance thresholds were set at P ≤ 0.05. (A) Significant correlations between motor recovery and theta–gamma PAC changes at the C3 and C4 electrodes (UEFM: r = 0.51, 0.49 and P = 0.0001, 0.0002; AMAT: r = 0.52, 0.39 and P = 0.0001, 0.004; MI: r = 0.33 and P = 0.02). Other measures showed no significant correlations (MI: r = 0.02 and P = 0.88; Grip: r = 0.06, 0.13 and P = 0.68, 0.35; Elbow MAS: r = 0.03, 0.15 and P = 0.84, 0.28; Wrist MAS: r = −0.22, 0.23, and P = 0.12, 0.10). (B) No significant correlations have been detected between motor recovery and beta–gamma PAC changes at the F3 and F4 electrodes (UEFM: r = −0.07, −0.10, and P = 0.62, 0.48; AMAT: r = −0.15, −0.19, and P = 0.29, 0.16; MI: r = −0.22, 0.12 and P = 0.12, 0.42; Grip: r = −0.16, 0.21 and P = 0.26, 0.14; Elbow MAS: r = −0.17, −0.13, and P = 0.23, 0.38; Wrist MAS: r = 0.07, −0.04, and P = 0.62, 0.80). Y-axis, PAC change; X-axis, motor score change. MI, modulation index; UEFM, upper extremity Fugl-Meyer; AMAT: Arm Motor Ability Test; MAS: modified Ashworth Scale.