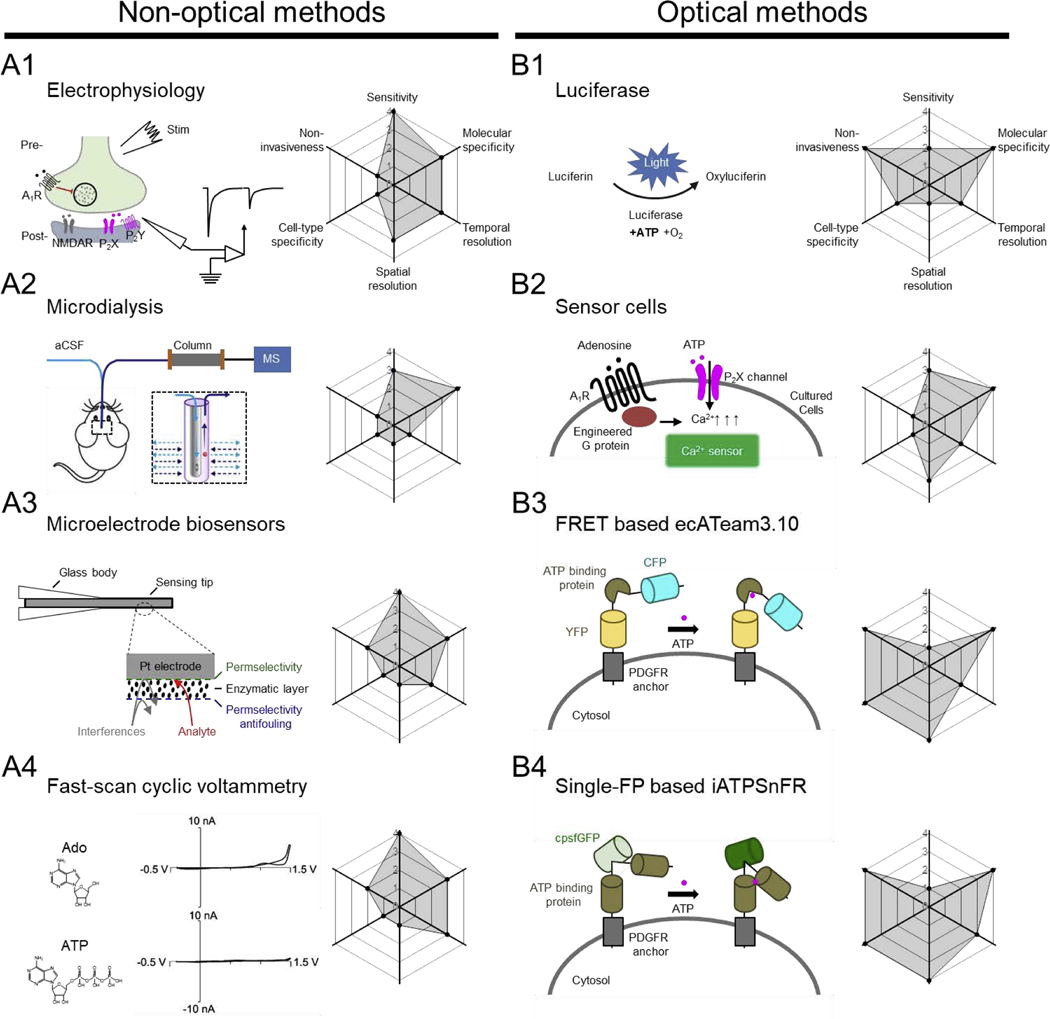
Fig. 1. Overview of select non-optical and optical methods for detecting purinergic transmitters.
In each panel, the principle (with example data, where indicated) behind for each method is shown at the left; the corresponding radar graph summarizing the method’s performance index (including sensitivity, molecular specificity, cell-type, non-invasiveness, spatial resolution, and temporal resolution) is shown at the right, with arbitrary units ranging from 0 to 4. Abbreviations: aCSF, artificial cerebrospinal fluid; Ado, adenosine; ATP, adenosine triphosphate; CFP, cyan fluorescent protein; FRET, fluorescence resonance energy transfer; IgK, light chain kappa; MS, mass spectrometry; NMDAR, N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor; PDGFR, platelet-derived growth factor receptor; YFP, yellow fluorescent protein. Schematic shown in (A3) adapted from (Dale and Frenguelli, 2012); data shown in (A4) adapted from (Swamy and Venton, 2007); schematic shown in (B3) adapted from (Conley et al., 2017); schematic shown in (B4) adapted from (Lobas et al., 2019).