Table 1. Rheologic and physicochemical characteristics of HA fillers measured in vitro.
| Parameters | Definitions | Relevance |
|---|---|---|
| Complex modulus 11 17 20 | G*, or hardness, measures overall viscoelastic properties of a gel. |
For most HA fillers, G* and G' are similar. The value of G* is derived from the formula
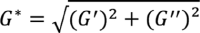 .
.
|
| Elastic modulus 11 17 20 | G′, or elasticity, measures the elastic properties of the gel and its ability to recover its shape after shearing stress is removed. | The most common descriptor for HA fillers, G′ is a measure of the strength (firmness). G′ is influenced by the degree of crosslinking and total HA concentration. |
| Viscous modulus 11 14 17 20 | G″, or loss modulus, measures the viscous properties of the gel and its inability to recover its shape. | HA fillers tend to have low G″. |
| Tan delta (δ) 11 17 20 24 | Tan δ is the ratio between the viscous and the elastic components of the HA gel (G″/G′). | Tan δ characterizes whether the gel is more viscous or more elastic (proportion of G″ to G′). Tan δ is usually low in crosslinked HA fillers, meaning that the elastic behavior under low shear stress is dominant over the viscous behavior. |
| Gel cohesion (cohesivity) 11 17 | Cohesivity measures the resistance to vertical compression/stretching. | This property characterizes how a filler behaves as a gel deposit once it is injected and subjected to forces. Gel cohesion is influenced by HA concentration and the crosslinking and sizing/homogenization of the gel. |
| Water uptake 7 11 | Water uptake, or swelling factor, measures the ability of the gel to swell from water uptake. | Water uptake/swelling factor helps anticipate the initial volumization of an implanted gel. It is influenced by the degree of crosslinking and HA concentration. |
| HA concentration 7 11 | This parameter is the total amount of HA found in the filler, expressed as mg/mL, and includes insoluble and soluble HA. | Insoluble HA is the crosslinked HA and the foundation for the effectiveness and durability of the filler. Soluble HA is the noncross-linked and rapidly degradable form of HA (from HA fragments, or usually added for facilitating extrusion). HA concentration impacts all the parameters. |
Abbreviation: HA, hyaluronic acid.
