Figure 5. The role of ISGs at the maternal/fetal interface.
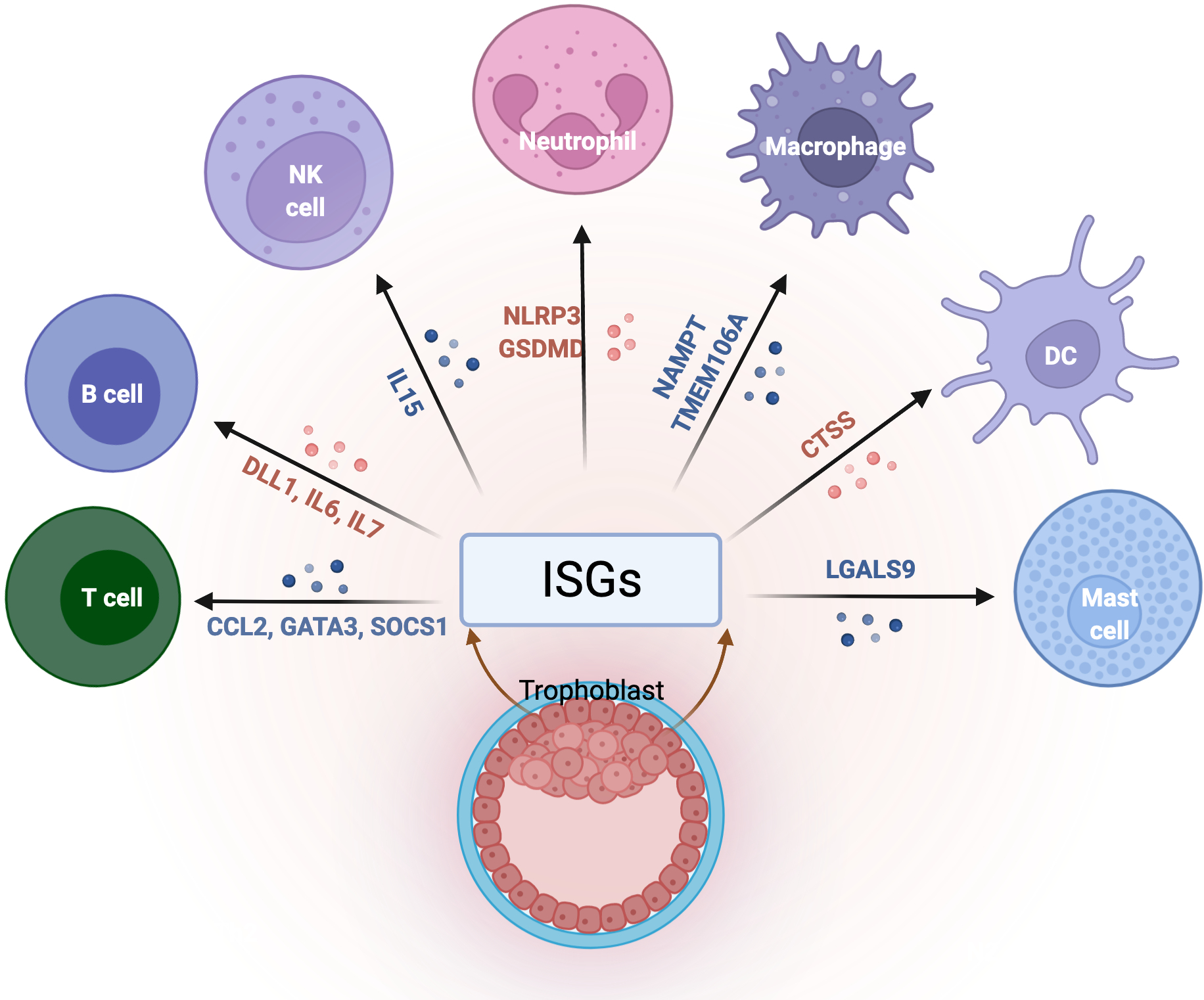
Immune cells present at the maternal-fetal interface display unique characteristics necessary for the support of pregnancy, and the trophoblasts plays a critical role in the regulation of their function and differentiation. Trophoblast secreted ISGs modulate immune cells functions and maintains tissue homeostasis at the maternal-fetal interface by preserving tolerance to paternal antigens as well as protection against infections.
Infections that affect ISGs expression in trophoblast cells will disrupt the immunological balance, leading to pregnancy complications. </p/> NK, natural killer; DC, dendritic cells; ISGs, interferon stimulated genes; IL, interleukin; CCL2, C-C motif chemokine ligand 2; GATA3, GATA binding protein 3; SOCS1, suppressor of cytokine signaling 1; DLL1, delta like canonical notch ligand 1; NLRP3, NLR family pyrin domain containing 3; GSDMD, gasdermin D; NAMPT, nicotinamide phosphoribosyltransferase; TMEM106A, transmembrane protein 106A; CTSS, cathepsin S; LGALS9, galectin 9. Figure created with BioRender.com
