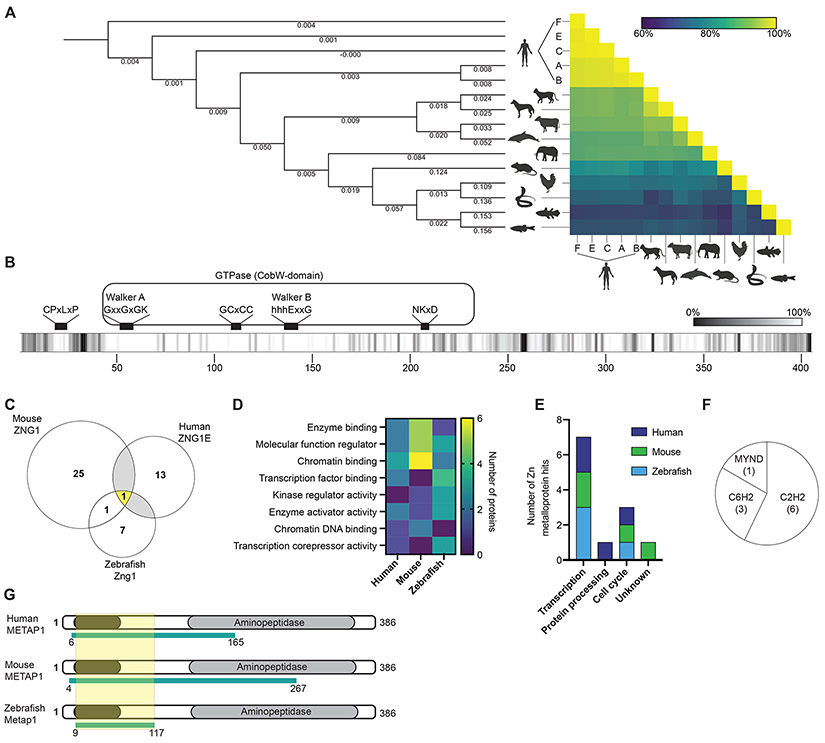
Figure 1. Identification of metalloprotein targets of Zn regulated GTPase metalloprotein activator 1 (ZNG1) in vertebrates.
(A) Cladogram and analysis of ZNG1 protein sequence conservation in vertebrates. Numbers on branches denote nucleotide substitutions per site. (B) Amino acid conservation along the length of vertebrate ZNG1s indicates high sequence conservation particularly in the GTPase domains and at the N-terminus. Lighter shading reflects higher conservation. (C) Yeast-two-hybrid screens using full-length human, mouse, and zebrafish ZNG1s identify unique and shared interacting proteins. (D) Molecular function enrichment analysis of ZNG1 interaction protein PFAM domains. (E) Number and cellular activity of ZNG1 client Zn metalloproteins detected in yeast-two-hybrid screens. (F) ZNG1 zf interaction domains in Zn metalloproteins shown in E. (G) Conserved ZNG1 interaction domain of METAP1 across species overlaps with a C6H2 domain. Yellow shading indicates minimal conserved region. See also Figure S1 and Table S1.