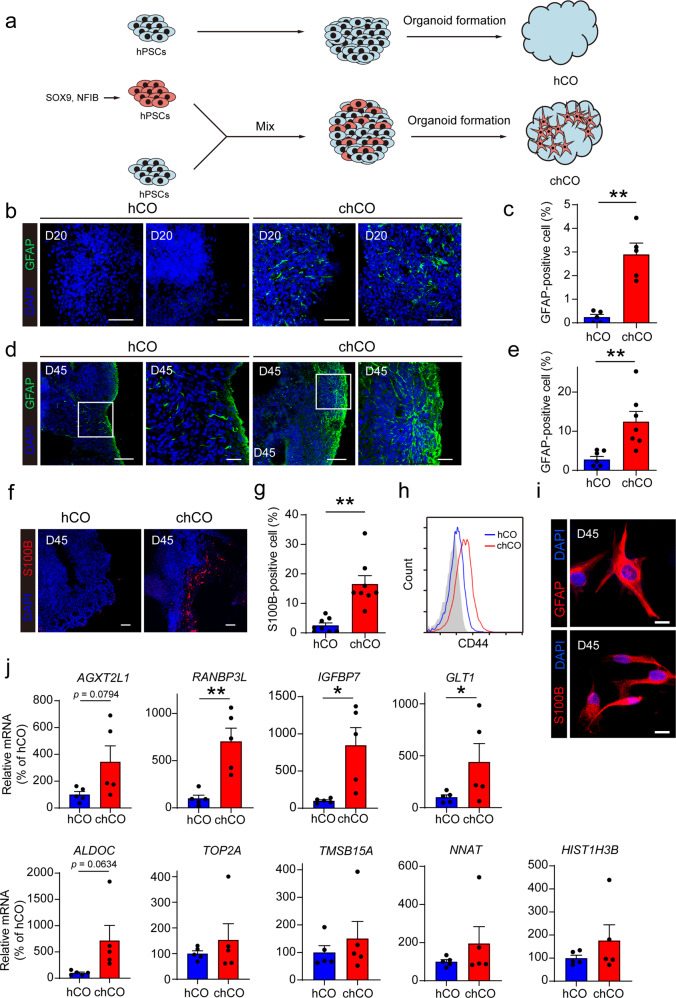
Fig. 1.
Induction of astrocytes in human cerebral organoids by Sox9 and NFIB expression. a Experiment procedure for generation of chCOs and control hCOs. b, c Immunostaining of chCOs and control hCOs on D20 for GFAP. Shown in c is the quantification of the percentage of the GFAP-positive area over the whole organoid area. Data represent the mean ± s.e.m. (n = 5 organoids, from three different batches; **p < 0.01). Scale bars in b: 50 µm. d, e Immunostaining of chCOs and control hCOs on D45 for GFAP. Shown in e is the quantification of the percentage of the GFAP-positive area over the whole organoid area. Data represent the mean ± s.e.m. (n = 7 organoids, from three different batches; **p < 0.01). Scale bars in d: left image 100 µm, right image 30 µm for hCOs and chCOs, respectively. f, g Immunostaining of chCOs and control hCOs on D45 for S100B. Shown in g is the quantification of the percentage of the S100B-positive area over the whole organoid area. Data represent the mean ± s.e.m. (n = 8 organoids, from three different batches; **p < 0.01). h Flow cytometry analysis of CD44 expression of chCO and control hCO cells. i Immunostaining of astrocyte-lineage cells purified from chCOs on D45 for GFAP and S100B. Scale bars, 20 µm. j qPCR analysis of mature and fetal astrocyte gene expression of chCO and control hCO cells. Data represent the mean ± s.e.m. (n = 5 different batches; *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01)