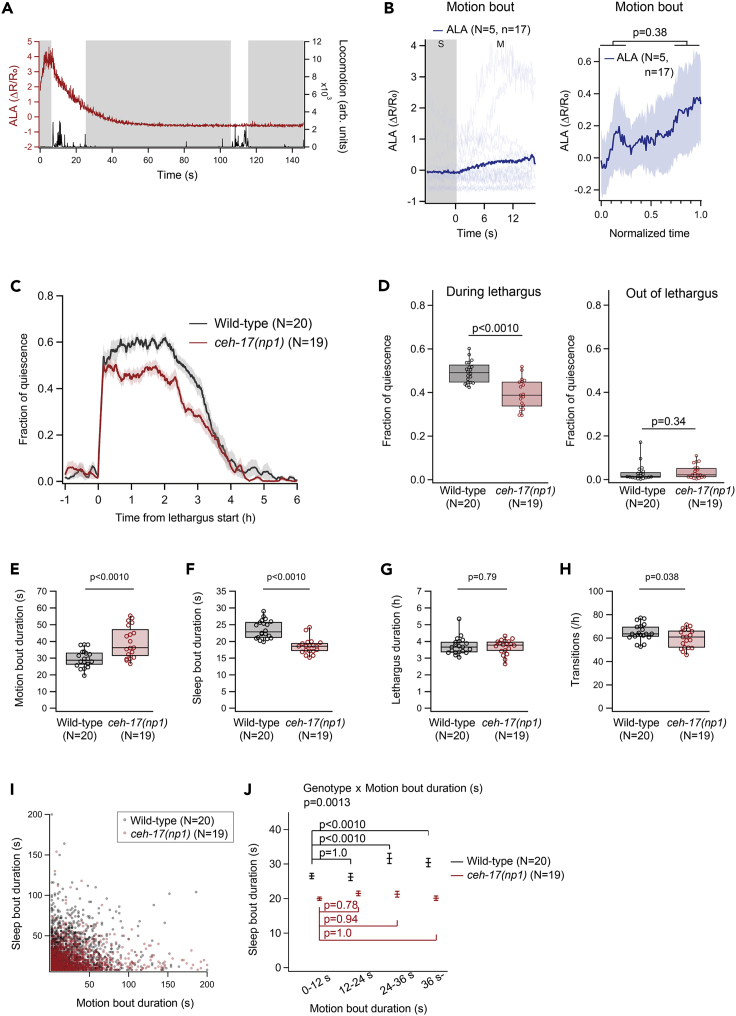
Figure 3.
CEH-17 dysfunction leads to abnormal ALA Ca2+ dynamics and impaired sleep homeostasis
(A) Representative pattern of Ca2+ activity (red) and locomotor activity (black) in a ceh-17(np1) mutant (SLP930 ceh-17(np1); lite-1(ce314); wtfIs5[Prab-3:: NLS::GcaMP6s + Prab-3::NLS::tagRFP]). Gray areas represent sleep bouts.
(B) Dynamics of ALA Ca2+ activity during motion bouts in the ceh-17(np1) mutant (SLP930 ceh-17(np1); lite-1(ce314); wtfIs5[Prab-3:: NLS::GcaMP6s + Prab-3::NLS::tagRFP]). (Left) Individual (light blue) and averaged (dark blue) traces. (Right) Averaged dynamics of Ca2+ activity. Here, the duration of each sleep or motion bout was normalized to 1. Shaded areas indicate ±SEM. p-values in Wilcoxon signed-rank test are indicated.
(C) Averaged patterns of fraction of quiescence around lethargus in wild-type (black) and ceh-17(np1) mutant (red). Shaded areas indicate ±SEM.
(D) Comparison of the average fraction of quiescence during lethargus (left) and after lethargus (right). p-values in the t test (left; during lethargus) and the Mann-Whitney’s U test (right; out of lethargus) are indicated.
(E–H) Comparison of the average durations of motion bouts (E) and sleep bouts (F), the total length of lethargus (G), and the number of transitions between motion and sleep bouts (H). p-values in the t test (E, F, and H) and the Mann-Whitney’s U test (G) are indicated.
(I) Sleep bout duration plotted against the prior motion bout duration in wild-type (black) and ceh-17(np1) mutants (red).
(J) Comparisons of the distribution of sleep bout durations based on the duration of the prior motion bouts in wild-type (black) and ceh-17(np1) mutants (red). Error bars indicate ±SEM. p-value in the interaction between genotype and motion bout duration in two-way ANOVA is indicated above the graph. p-values in the multiple comparison with Sidak correction are indicated in the graph. N and n in the figure represent numbers of animals and bouts, respectively.