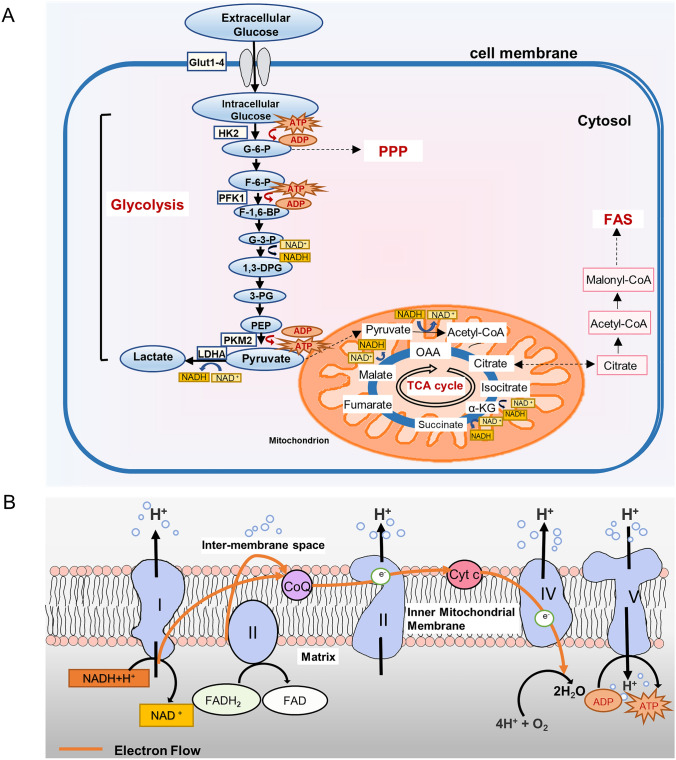
Fig. 1.
Simplified representation of glucose metabolic pathways. A Glycolysis occurs in the cytoplasm, converting glucose into pyruvate and then into lactic acid in the mitochondria. Under aerobic conditions, pyruvic acid is oxidized and decarboxylated to form acetyl CoA, which can be completely oxidized into TCA. Intermediates in glucose metabolism can flow to other metabolic pathways, such as PPP and FAS. B ETC refers to the structure of NADH or FADH2 transferring electrons to oxygen. OXPHOS causes the gain and loss of electrons on the electron carrier, which is transferred between redox substrates to form ETC