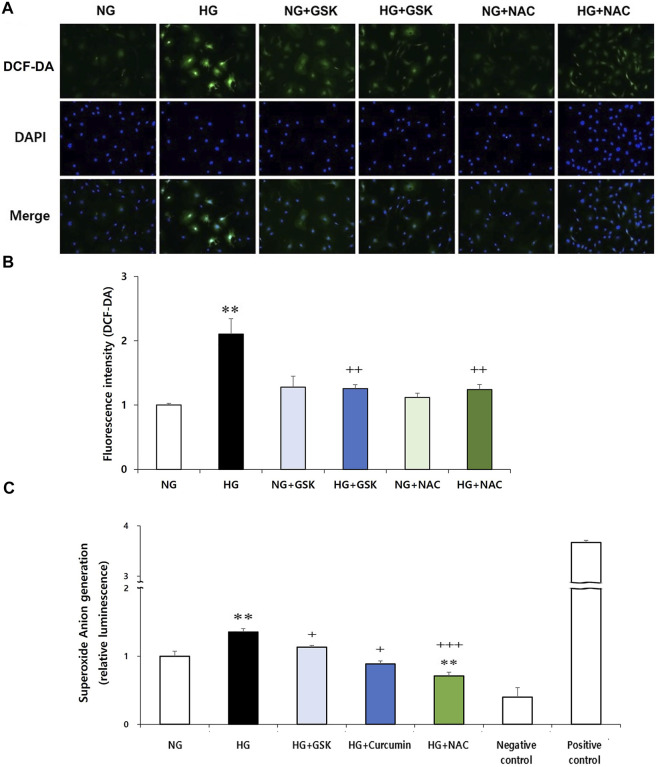
FIGURE 6.
GSK′872 or NAC treatment reduces intracellular ROS expression in high glucose-treated podocytes. DCF-DA-sensitive intracellular ROS was observed (A) and quantified (B) after treating the podocytes under six different conditions for 24 h: NG (5.6 mM D-glucose), HG (30 mM D-glucose), NG + GSK (5.6 mM D-glucose + 10 µM GSK′872), HG + GSK (30 mM D-glucose + 10 µM GSK′872), NG + NAC (5.6 mM D-glucose + 50 μM N-acetyl cysteine), and HG + NAC (30 mM D-glucose + 50 μM N-acetyl cysteine). In GSK- or NAC-treated groups, HG-induced intracellular ROS expression was significantly reduced (A,B). NG, normal glucose; HG, high glucose; ROS, reactive oxygen species; GSK, GSK′872. **, p < 0.01 versus NG; ++, p < 0.01 versus HG. Superoxide anion was measured using a luminometer. After starvation for 24 h, drug treatment was performed for 16 h (C). High glucose-induced superoxide anion production in podocytes was significantly reduced by curcumin, GSK′872, and NAC. Negative control, assay buffer + xanthine oxidase + SOD; positive control, assay buffer + xanthine oxidase. **, p < 0.01 versus NG; +, p < 0.05, ++, p < 0.01 versus HG.