FIGURE 7.
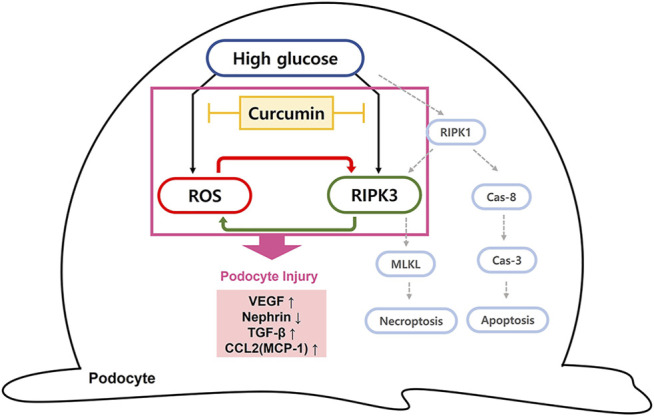
Diagram of curcumin suppressing intracellular ROS and RIPK3 expression in high glucose-treated podocytes. Schematic representation of the possible signaling pathway leading to podocytopathy by high glucose. We suggest that the elevated hyperglycemia condition can induce the intracellular ROS generation and increase RIPK3 expression, resulting in podocytopathy through inflammatory response and fibrosis. Curcumin administration protects against podocyte injury by inhibiting ROS generation and downregulating RIPK3. Due to a cross-stimulating relationship between the two, the reduced level of each further contributes to the suppression effect of curcumin on intracellular ROS and RIPK3 expression. RIPK3 inhibition prevents necroptosis of podocytes since it prevents phosphorylation and aggregation of MLKL to proceed the final stage of necroptosis. Cas-8, caspase-8; Cas-3, caspase-3; MLKL, mixed lineage kinase domain-like protein.
