Figure 1.
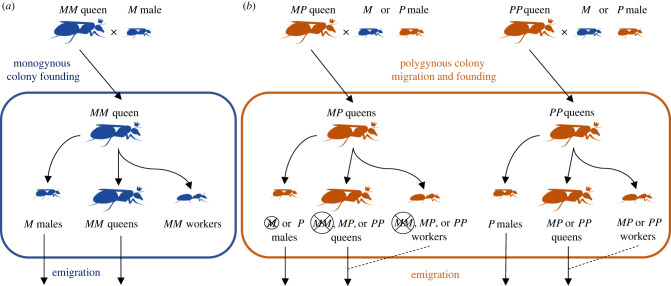
Social and genetic system of F. selysi. (a) Mature monogynous colonies contain a single MM queen mated with M males. The queen produces M males (haploid, from unfertilized eggs), as well as MM queens and MM workers (diploid, from fertilized eggs). The offspring (males and queens) fly out of the colony for mating, and queens establish colonies independently. (b) Mature polygynous colonies contain multiple MP or PP queens mated with M or P males. The offspring (queens and males) also fly out of the colony for mating. MP and PP queens (and possibly MM queens mated to P males) may establish colonies independently, or, for polygynous queens, with the help of workers from their natal colony (dashed line). The P haplotype acts as a maternal-effect killer, so that all offspring of MP queens that do not inherit the P haplotype die during development. As a result, M males and MM females are never produced by polygynous colonies. (Online version in colour.)