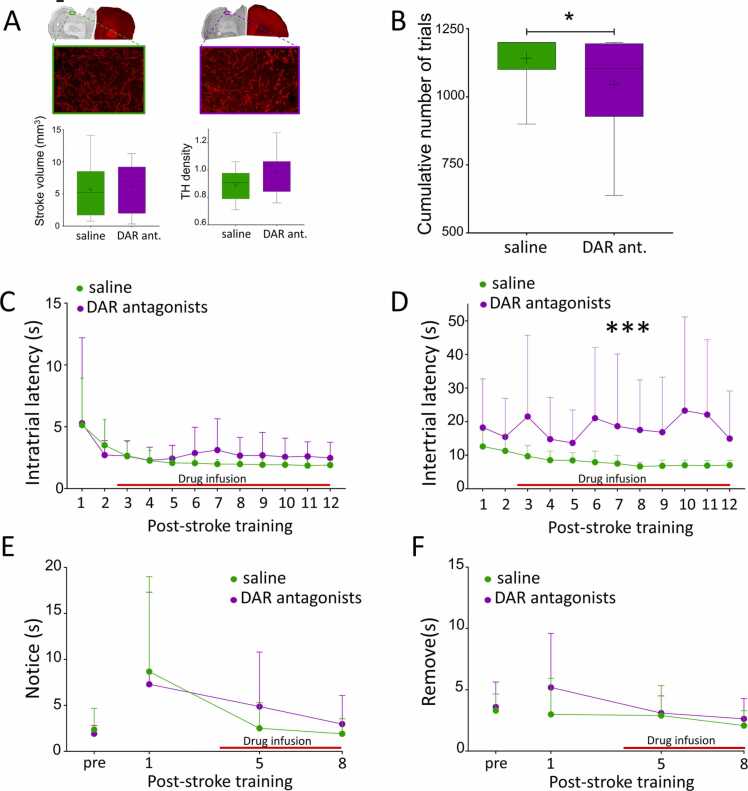
Fig. 2.
DA antagonists alter motivation after stroke. A. Anatomical characterization of the stroke volume and TH innervation of the peri-infarct area. Analysis of stroke volume and TH innervation of the peri-infarct area (green: saline n = 10, purple: DAR antagonists n = 7) revealed no difference. Scale bar= 1 mm for upper panel, 1 µm for lower panel. B. Effects of DAR antagonists on training intensity. Rats treated with DAR antagonists (purple, n = 16) performed significantly fewer trials during the 12 days of post-stroke training than saline treated rats (green, n = 18). * : p < 0.05. C. Effects of DAR antagonists on intratrial latency. DAR blockade did not impair the speed of execution of a trial compared to saline. D. DAR antagonists increased intertrial latencies. DAR antagonist-treated rats took significantly longer to initiate a new trial than saline treated rats. *** : p < 0.001. E-F. Effect of DAR antagonists on somatosensory function. No difference was detected between saline (green, n = 16) and DAR antagonists (purple, n = 12) on the time to notice (E) or to remove (F) a piece of tape placed on the lesioned forelimb. A, B: Boxes: median, 25th and 75th percentile. Whiskers: 5th and 95th percentile. + : sample mean. C-F: Red line: timecourse of drug infusion. (For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.)