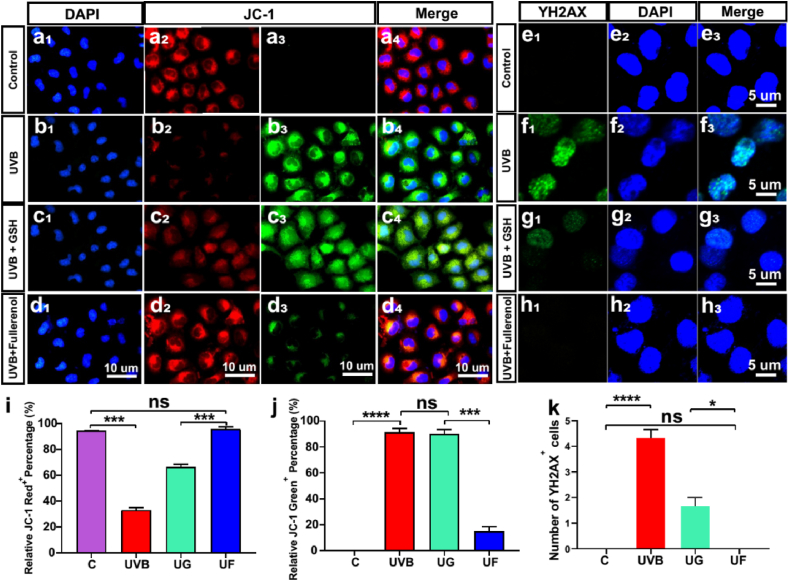
Fig. 9.
Effects of fullerenol or GSH on mitochondrial membrane potential changes and DNA damage in hCECs caused by UVB exposure. a-d) Fluorescence changes of different mitochondrial membrane potentials in cells after different exposures. Normal mitochondria were fluorescently labeled in red and the fluorescence changes from green to red when the mitochondrial membrane potential decreases. a1-a3) Control group. b1-b3) hCECs exposed to UV for 2 h. c1–c3) hCECs treated with 6.8 μg/ml GSH after exposure to UV for 2 h. d1-d3) hCECs were treated with 25 μg/ml fullerenol for 24 h. e-h) Representative images of immunofluorescence for the γ-H2AX positive cells (green, counterstained with DAPI, blue) in hCECs. e1-e3) Control group.f1–f3) hCECs exposed to UV for 2 h. g1-g3) hCECs treated with GSH for 24 h. h1–h3) hCECs were treated with fullerenol for 24 h after being exposed to UV radiation for 2 h. i) Comparison of the number of JC-1+ red cells in different groups. j) Comparison of the number of JC-1+ Green cells in different groups. k) Comparison of the number of γ-H2AX-positive cells in different groups. N = 3 samples per group. Data were expressed as the mean ± SEM from three independent experiments. *P < 0.1, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001 using one-way ANOVA and post-hoc Tukey's test. (For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the Web version of this article.)