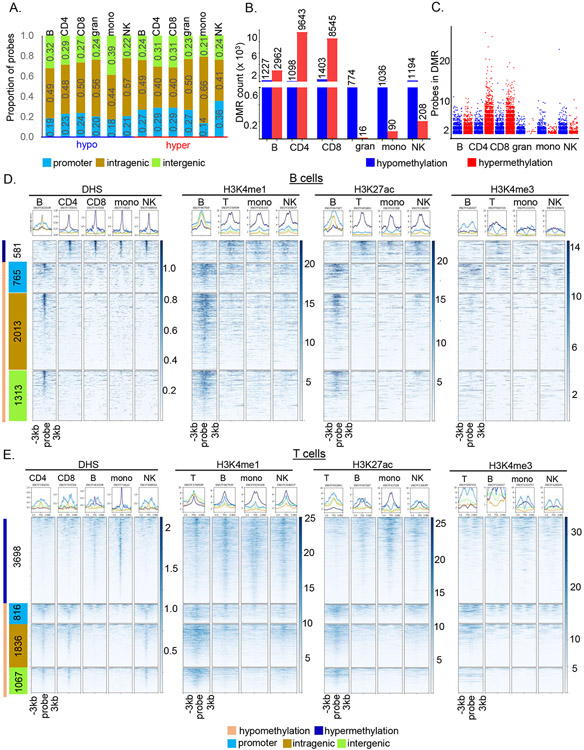
Figure 2. Cell-specific sites of differential methylation coincide with other cell-specific epigenetic marks.
A) Distribution of cell-specific hypo- and hypermethylated probes at promoters (< −1500bp/5’UTR, blue), intragenic regions (exon/intron/3’UTR, ochre) and intergenic regions (green).
B) Cell-specific DMRs were defined by two or more hypo- or hypermethylated cell-specific probes located within 300bp. Hypo- (blue) and hypermethylated (red) DMR numbers in each cell type are indicated above the bars.
C) Probe counts in cell-specific hypo- (blue) or hypermethylated (red) DMRs. Each dot represents the number of probes present in a cell-specific DMR. The minimum number of probes in a DMR is two.
D) Relationship of B cell-specific hypo- and hypermethylated probes to other epigenetic marks. Data for DNase hypersensitive sites (DHS) and histone modifications in the indicated cell types was obtained from the ENCODE database. Only DHS data was available for CD4+ and CD8+ T cells individually; for all histone modifications ‘T’ refers to total T cells, ‘mono’ to monocytes and ‘NK’ to natural killer cells. Summary plots (top) and heatmaps (bottom) show the peak intensity of DHS or histone marks in ± 3kb region surrounding each B cell-specific hyper- (dark blue bar on the left) and hypomethylated (light orange bar on the left) site. Hypomethylated probes were further grouped into promoter (blue), intragenic (ochre) and intergenic regions (light green) following definitions in part A. Number of probes in each category are indicated within colored boxes. Corresponding patterns for all innate cell types are shown in Figure S3.
E) Relationship of T cell-specific hypo- and hypermethylated probes to other epigenetic marks. Data for DNase hypersensitive sites (DHS) and indicated histone modifications was obtained from the ENCODE database and labeled as in D.