Figure 4.
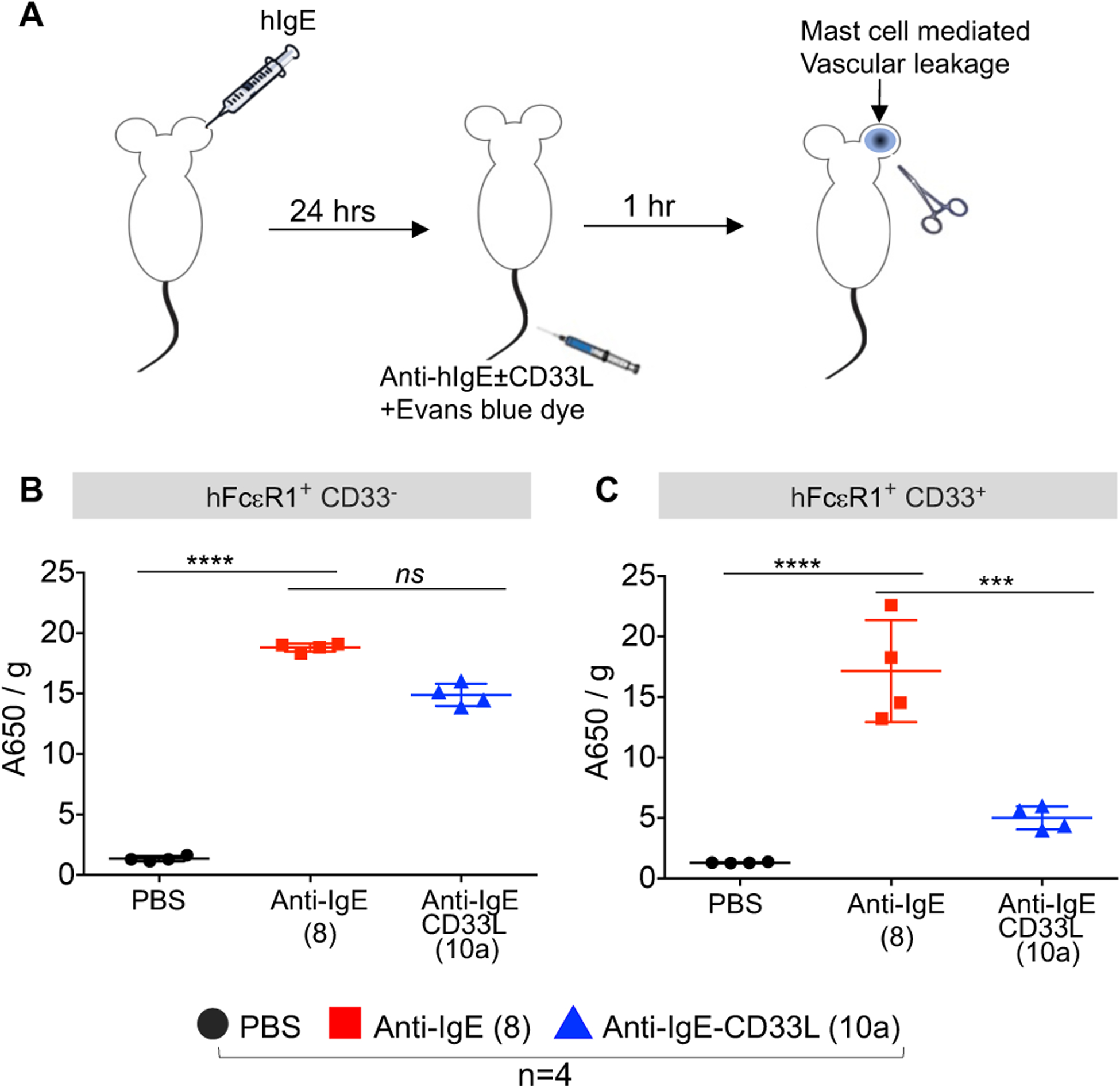
Impact of CD33L conjugation to anti-IgE on the induction of passive cutaneous anaphylaxis (PC) in the mouse ear. (A) Schematic representation of PC assay. One ear of each mouse is sensitized with hIgE (1μg/mice) followed by intravenous injection (i.v.) one day later with 0.2 ml of PBS containing Evans blue dye to detect vascular leakage, and either no antibody (PBS) or 10 μg of either anti-IgE (8) or anti-IgE-CD33L (10a). After 1h treated ears were removed and assessed for anaphylaxis by extracting the blue dye (OD A460/g tissue). (B) Assessment of anaphylaxis induced in hFcεRI+ × hCD33− mice. (C) Assessment of anaphylaxis induced in hFcεRI+ × hCD33+ mice. Results in B-C were analyzed by one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s multiple comparison test (***P< 0.001 and ****P< 0.0001).
