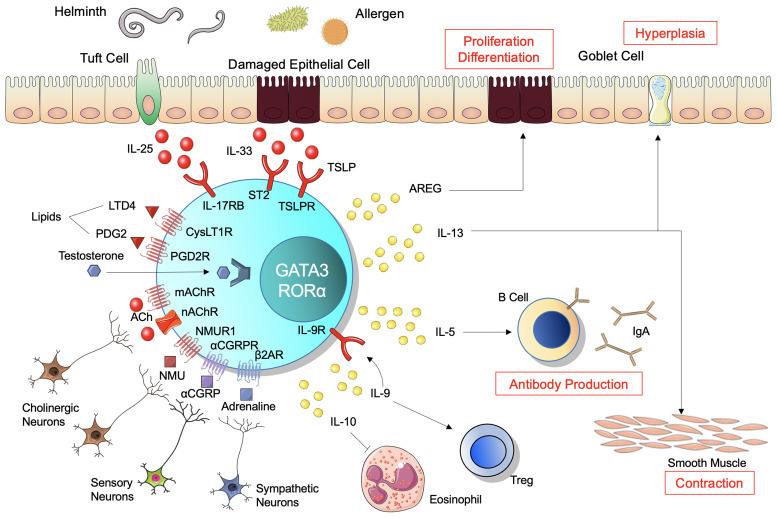
Figure 1.
Regulation and function of ILC2. Alarmins, IL-25, IL-33, and thymic stromal lymphopoietin (TSLP), activate innate lymphoid cells 2 (ILC2) to expand and produce cytokines. Neural systems regulate ILC2s bidirectionally through neuropeptides and neurotransmitters. ILC2s require transcription factors GATA3 and RORα, and subsequently produce various cytokines. IL-13 induces hyperplasia of goblet cells and contraction of smooth muscle in the intestine, involved in clearance of antigens in the lumen. IL-5 regulates B-cell antibody production and enhances IgA production. Amphiregulin (AREG) promotes epithelial cell proliferation and differentiation. IL-9 and IL-10 contribute to resolution of inflammation, while IL-9 also promotes regulatory T-cell activation and IL-10 decreases eosinophil recruitment. ILC2 expresses IL-9 receptor and thus receives IL-9 autocrine feedback. Regarding ligands and receptors, red indicates activation, blue indicates inhibition, and purple indicates both functions.