FIGURE 2.
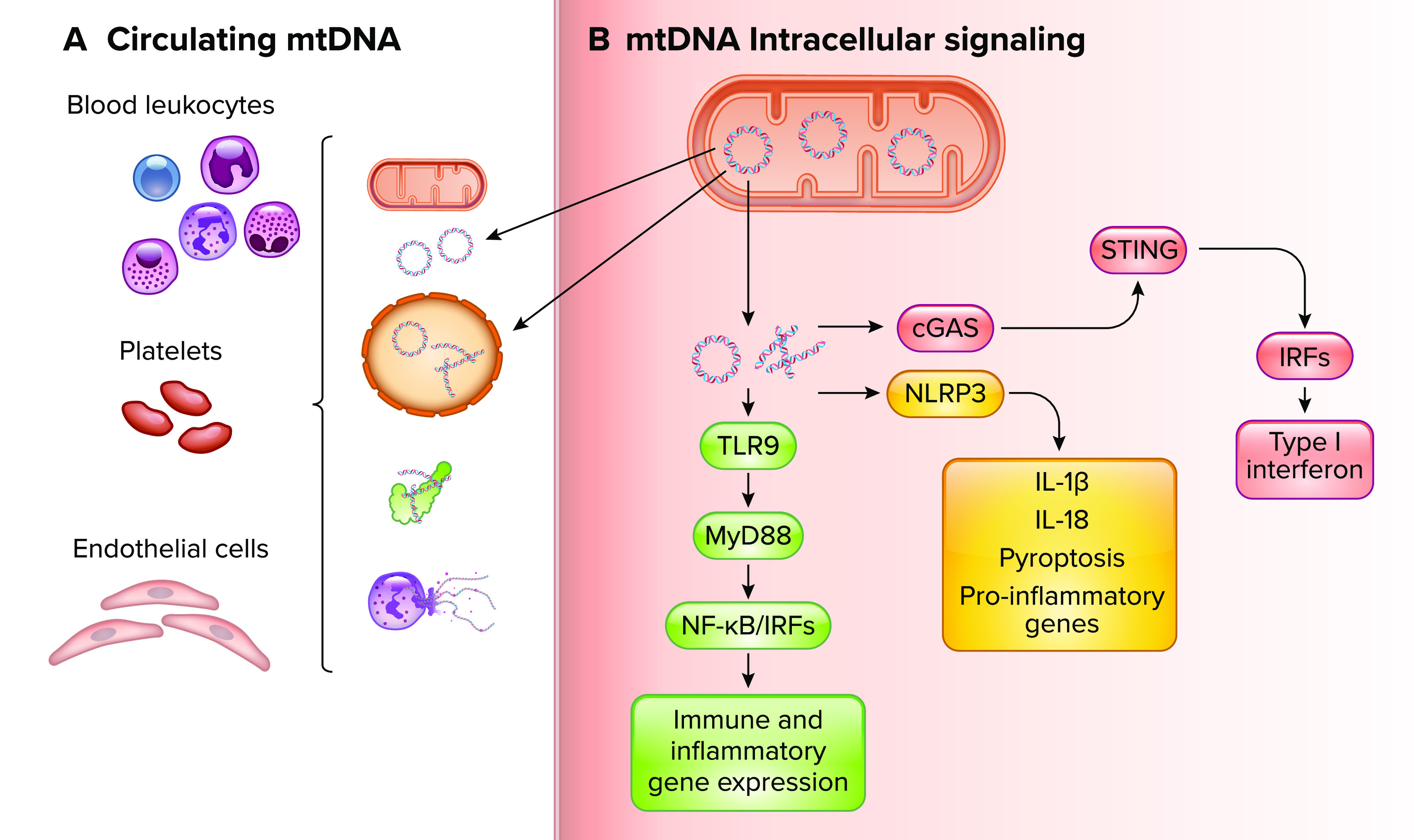
Recognition of various biological forms of circulating cell-free mitochondrial DNA in maternal circulation and mtDNA-induced intracellular proinflammatory signaling by diverse innate immune system receptors A: biological forms of ccf-mtDNA include mtDNA confined to whole mitochondria and extracellular vesicles, extruded from neutrophils in neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs), and in circular or fragmented biological forms complexed to other mitochondrial-associated proteins such as mitochondrial transcription factor A. These various biological forms can be recognized by leukocytes, platelets, and endothelial cells in the maternal circulation. B: intracellular mtDNA-induced proinflammatory signaling mechanisms contributing to innate immune system activation and release of mtDNA into the maternal circulation. TLR9, Toll-like receptor 9; MyD88, myeloid differentiation primary response gene 88; NF-κB, nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells; IRFs, interferon regulatory factors; NLRP3, nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain, leucine-rich repeats, and pyrin domain-containing protein 3; IL, interleukin; cGAS, cyclic guanosine monophosphate-adenosine monophosphate synthase; STING, stimulator of interferon genes. Image created with BioRender.com and used with permission.
