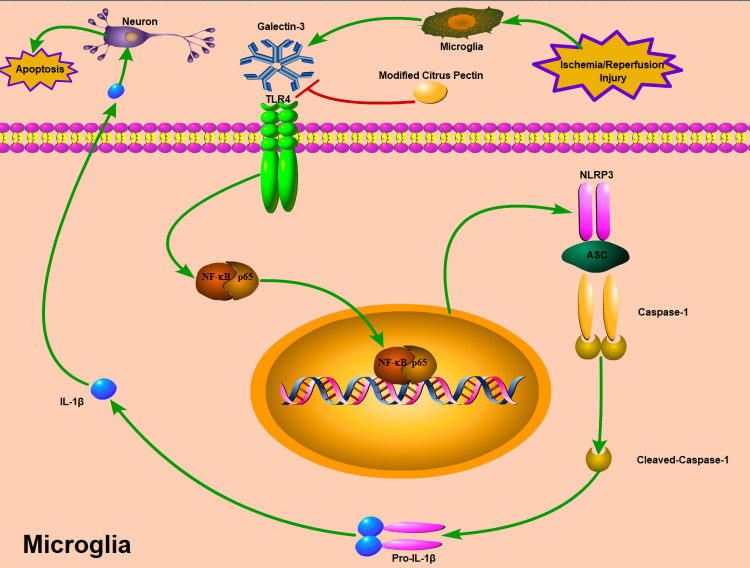
Figure 12.
Potential mechanisms by which MCP protects against cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury. MCP indicates modified citrus pectin. Cerebral ischemic insult may promote the expression of galectin-3 in microglia, and then trigger the activation of NLRP3 inflammasome in microglia through TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway, which converts caspase-1 into cleaved-caspase-1. Cleaved-caspase-1 further converts pro-IL-1β into IL-1β, which is then secreted into the extracellular space and contributes to secondary inflammatory response. The neuroprotective effects of MCP on anti-inflammation through blocking expression of galectin-3 was mediated by the axis of TLR4/NF-κB/NLRP3/cleaved-caspase-1/IL-1β in microglia.