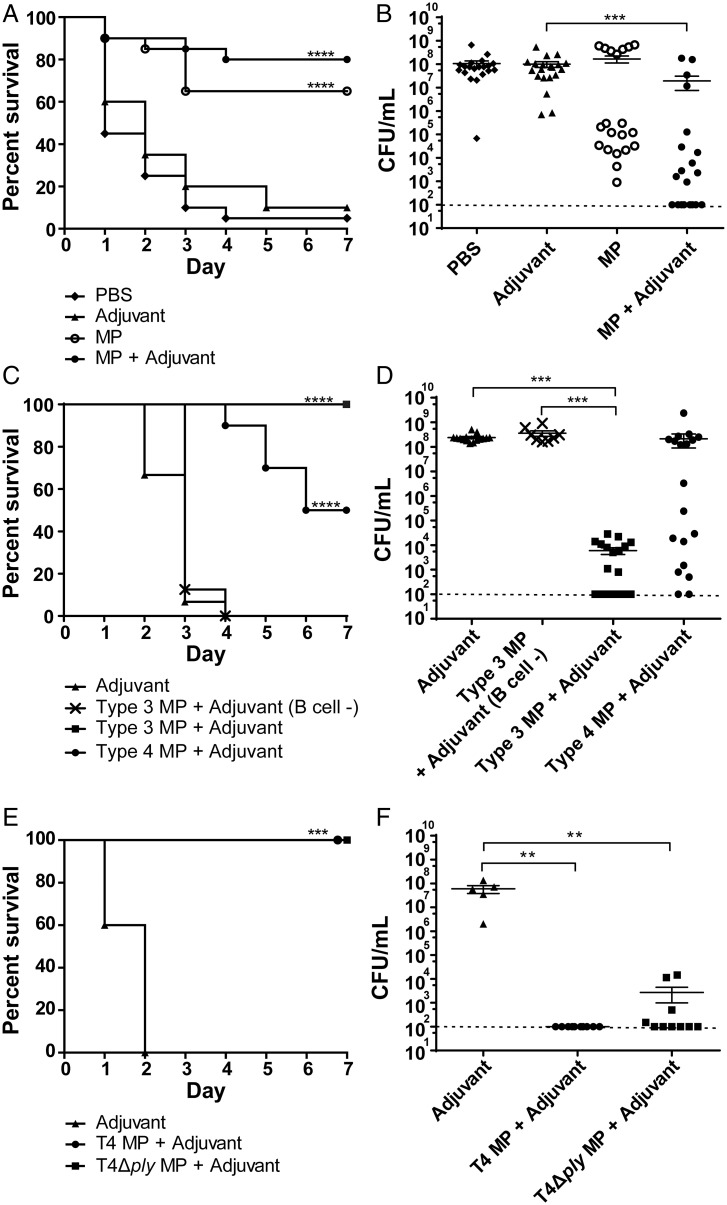
Fig. 1.
Intranasal immunization with MPs confers protection against intranasal pneumococcal infection. (A and B) T4 MPs confer cross-protection against infection with a serotype 1 strain. (A) Intranasal immunization of C57BL/6 mice with MPs from strain T4 of serotype 4 and subsequent infection with strain BHN733 of serotype 1 resulted in 80% survival; 20 mice per group. (B) Bacteria (in CFUs) in the lungs of immunized and infected mice in A after sacrifice. Each dot represents one mouse. (C and D) Immunization with MPs of serotype 3 confers antibody-dependent protection against intranasal infection with the same strain. (C) Percentage of mice that survived the intranasal infection with serotype 3 bacteria of WT C57BL/6 mice or of B cell–deficient mice (muMt knockout mice) immunized with MPs from the same serotype 3 strain BHN428 or of WT mice immunized with MPs from the serotype 4 strain T4; 20 mice per group. (D) Number of bacteria (CFUs) in the lungs of mice from C at sacrifice. Each dot represents one mouse. (E and F) Protection conferred by MPs against intranasal pneumococcal challenge is not dependent on the cholesterol-binding cytotoxin Ply. (E) Percentage survival after intranasal infection with T4 of WT C57BL/6 mice immunized with MPs from T4 or its Ply-deficient strain T4Δply; 10 mice per group, 5 mice immunized with adjuvant as control. (F) Number of bacteria (CFUs) in the lungs of mice at sacrifice. Each dot represents one mouse. Error bars represent the standard error of the mean (SEM). Dashed horizontal line in (B, D, and F) represents the limit of detection for the lung CFU counts using this method. **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; ****P < 0.0001.