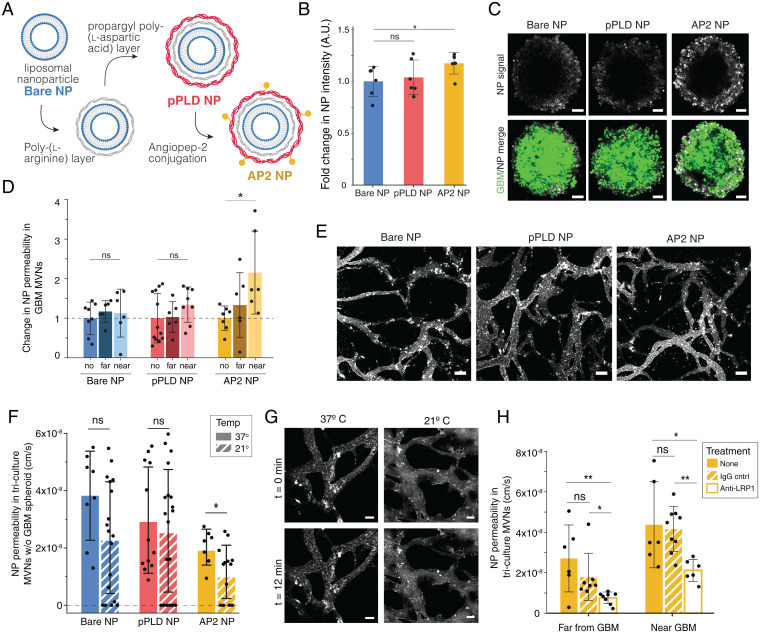
Fig. 2.
Functionalized LbL-NPs cross BBB MVNs near GBM spheroids via LRP1-mediated transport. (A) LbL assembly of AP2 NPs. (B) Fold change in mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) of NPs in GBM spheroids without vascular networks, normalized to bare NP; points represents n = 1 spheroid. (C) Representative GBM spheroids after 12-min NP incubation, as quantified in B. (Scale bars: 100 µm.) (D) NP permeability in networks with no GBM spheroid (no) and in regions near and far from a GBM spheroid, normalized to the no spheroid device; points represent n = 1 ROI; n = 6 devices per condition were considered. (E) Representative images of NPs in the BBB microvessels at t = 0 min following NP perfusion; time-lapse images over 12 min were used to determine permeabilities in D. (Scale bars: 100 µm.) (F) BBB vessel permeabilities to the three NP formulations in networks without GBM spheroids at 37 °C and 21 °C. Points represent n = 1 ROI; n = 4 devices per condition were considered. (G) Representative images of AP2 NPs at t = 0 and t = 12 min, as quantified in F. (Scale bars: 50 µm.) (H) BBB vessel permeabilities to AP2 NPs at 37 °C following incubation for 30 min with anti-LRP1 or IgG control antibodies. Points represent n = 1 ROI; for antibody conditions, n = 4 devices were considered; n = 6 nontreated devices. Throughout, bars represent mean ± SD. ns, not significant. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01. Statistical analyses are described in Materials and Methods. A.U., arbitrary units; w/o, without.